Similar image search for histopathology: SMILY
- PMID: 31304402
- PMCID: PMC6588631
- DOI: 10.1038/s41746-019-0131-z
Similar image search for histopathology: SMILY
Abstract
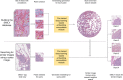
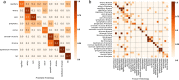
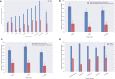
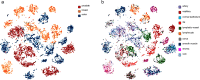
The increasing availability of large institutional and public histopathology image datasets is enabling the searching of these datasets for diagnosis, research, and education. Although these datasets typically have associated metadata such as diagnosis or clinical notes, even carefully curated datasets rarely contain annotations of the location of regions of interest on each image. As pathology images are extremely large (up to 100,000 pixels in each dimension), further laborious visual search of each image may be needed to find the feature of interest. In this paper, we introduce a deep-learning-based reverse image search tool for histopathology images: Similar Medical Images Like Yours (SMILY). We assessed SMILY's ability to retrieve search results in two ways: using pathologist-provided annotations, and via prospective studies where pathologists evaluated the quality of SMILY search results. As a negative control in the second evaluation, pathologists were blinded to whether search results were retrieved by SMILY or randomly. In both types of assessments, SMILY was able to retrieve search results with similar histologic features, organ site, and prostate cancer Gleason grade compared with the original query. SMILY may be a useful general-purpose tool in the pathologist's arsenal, to improve the efficiency of searching large archives of histopathology images, without the need to develop and implement specific tools for each application.
Keywords: Image processing; Machine learning; Medical imaging; Software.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsN.H., J.D.H., Y.L., E.R., D.S., M.T., C.J.C., C.H.M., P.Q.N., L.H.P., G.S.C. and M.C.S. are employees of Google LLC and own Alphabet stock. M.E.B. and M.B.A. were compensated for their expertize and time as pathologists.
Figures


References
-
- Lew MS, Sebe N, Djeraba C, Jain R. Content-based multimedia information retrieval: state of the art and challenges. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. 2006;2:1–19. doi: 10.1145/1126004.1126005. - DOI
-
- Google Images. https://images.google.com/. (Accessed 17 Jan 2019).
-
- Amazon Flow. A9. https://a9.com/what-we-do/visual-search.html. (Accessed 17 Jan 2019).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

