Machine learning detection of obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy using a wearable biosensor
- PMID: 31304403
- PMCID: PMC6591226
- DOI: 10.1038/s41746-019-0130-0
Machine learning detection of obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy using a wearable biosensor
Abstract
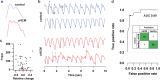
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a heritable disease of heart muscle that increases the risk for heart failure, stroke, and sudden death, even in asymptomatic patients. With only 10-20% of affected people currently diagnosed, there is an unmet need for an effective screening tool outside of the clinical setting. Photoplethysmography uses a noninvasive optical sensor incorporated in commercial smart watches to detect blood volume changes at the skin surface. In this study, we obtained photoplethysmography recordings and echocardiograms from 19 HCM patients with left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (oHCM) and a control cohort of 64 healthy volunteers. Automated analysis showed a significant difference in oHCM patients for 38/42 morphometric pulse wave features, including measures of systolic ejection time, rate of rise during systole, and respiratory variation. We developed a machine learning classifier that achieved a C-statistic for oHCM detection of 0.99 (95% CI: 0.99-1.0). With further development, this approach could provide a noninvasive and widely available screening tool for obstructive HCM.
Keywords: Diagnostic markers; Translational research.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsM.J.S. is an employee and owns shares in MyoKardia, Inc., a biotechnology company developing small molecules that target the sarcomere for the treatment of cardiomyopathies. R.vanM. and O.D. are employees and own shares in Wavelet Health. C.W. owns shares in MyoKardia, Inc. Support for these studies was provided by MyoKardia. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Machine learning detection of obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy using a wearable biosensor.NPJ Digit Med. 2019 Dec 10;2:120. doi: 10.1038/s41746-019-0186-x. eCollection 2019. NPJ Digit Med. 2019. PMID: 31840091 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

