Conformational profile, vibrational assignments, NLO properties and molecular docking of biologically active herbicide1,1-dimethyl-3-phenylurea
- PMID: 31304416
- PMCID: PMC6600072
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01987
Conformational profile, vibrational assignments, NLO properties and molecular docking of biologically active herbicide1,1-dimethyl-3-phenylurea
Abstract
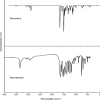
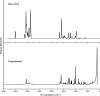
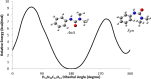
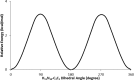
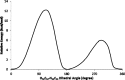
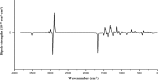
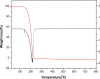
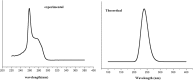
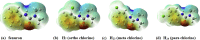
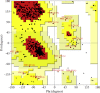
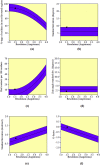
1,1-Dimethyl-3-phenylurea (known as fenuron) which is a phenyl urea-based widely used herbicide exhibits interesting structural and conformational properties and a notable biological activity. A detailed analysis on the vibrational, molecular and electronic characteristics of fenuron has been carried out. Potential energy scans (PESs) performed at the B3LYP/6-311++G(d,p) level of theory predicted two possible minima corresponding to the optimized anti and synforms resulting from the internal rotation about the N-C bond. The presence of an auxochrome together with the interaction with DMSO solvent exhibited a blue shift corresponding to the C=O orbitals. Delocalization of HOMO and LUMO orbital facilitated the charge transfer effect in the molecule. The calculated HOMO-LUMO energies, chemical potential, energy gap and global hardness suggested a low softness value for the compound while its biological activity was described by the value of electrophilicity. Chlorine substitution in the phenyl ring influenced the orbital delocalization for ortho and para substitutions but that of meta remained unaffected. NLO properties were noticed to increase due to chlorine substitution in the parent molecule. The docking results suggested that the compound exhibits an inhibitory activity against mitochondrial ubiquinol-cytochrome-c reductase and can be developed as a potential anticancer agent.
Keywords: DFT; Fenuron; Molecular docking; NBO; NLO; Organic chemistry; Pharmaceutical chemistry; Theoretical chemistry.
Figures


References
-
- Gangwar S.K., Rafiquee M.Z.A. Kinetics of the alkaline hydrolysis of fenuron in aqueous and micellar media. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 2007;39:638–644.
-
- Oturan M.A., Edelahi M.C., Oturan N., El K., Aaron J. Environmental kinetics of oxidative degradation/mineralization pathways of the phenylurea herbicides diuron, monuron and fenuron in water during the application of the electro-Fenton process. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2010;97:82–89.
-
- Tahmasseb L.A., Nelieu S., Kerhoas L., Einhorn J. Ozonation of chlorophenylurea pesticides in water, reaction monitoring and degradation pathways. Sci. Total Environ. 2002;291:33–44. - PubMed
-
- Gallard H., De Laat J. Kinetics of oxidation of chlorobenzenes and phenylureas by Fe(II)/H2O2 and Fe(III)H2O2, evidence of reduction and oxidation reactions of intermediates by Fe(II) or Fe(III) Chemosphere. 2001;42:405–413. - PubMed
-
- Mazellier D.L.J., Busset P., Delmont A. A comparison of fenuron degradation by hydroxyl and carbonate radicals in aqueous solution. Water Res. 2007;41:4585–4594. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

