The use of wastewater analysis in forensic intelligence: drug consumption comparison between Sydney and different European cities
- PMID: 31304443
- PMCID: PMC6610511
- DOI: 10.1080/20961790.2018.1500082
The use of wastewater analysis in forensic intelligence: drug consumption comparison between Sydney and different European cities
Abstract
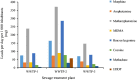
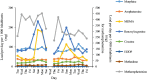
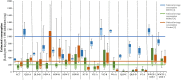
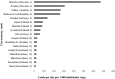
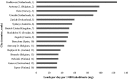
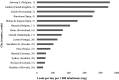
Wastewater analysis offers objective and complementary information to illicit drug agencies by monitoring patterns of illicit drug consumption. In this study, wastewater samples from three different wastewater treatment plants in Sydney, Australia were collected in March 2016. Ten targeted drugs were analysed and temporal and geographical analyses were performed to obtain a better understanding of the type and amount of illicit drugs consumed in Sydney in comparison with similar studies conducted around Australia and in Europe. Among the targeted drugs, methamphetamine was consumed the most, followed by cocaine and 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA). Weekly patterns were observed where a peak during the weekend was present. The geographical analysis showed differences between the regions targeted. This observation may be related to socio-demographic aspects. The comparison of our study to other data sources from Australia showed a high consumption of methamphetamine in Sydney and Western Australia. The comparison between Sydney and different European cities revealed a difference in consumption, which is in line with traditional market indicators. The information obtained through wastewater analysis provides complementary information regarding illicit drug consumption, the size, and the evolution of the illicit drug market. This, ultimately, will assist authorities in making informed decisions.
Keywords: Forensic sciences; forensic intelligence; illicit drug consumption; wastewater-based epidemiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The embodiment of wastewater data for the estimation of illicit drug consumption in Spain.Sci Total Environ. 2021 Jun 10;772:144794. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144794. Epub 2021 Jan 26. Sci Total Environ. 2021. PMID: 33770873
-
Spatial, temporal and socioeconomic patterns of illicit drug use in New Zealand assessed using wastewater-based epidemiology timed to coincide with the census.N Z Med J. 2021 Jun 25;134(1537):11-26. N Z Med J. 2021. PMID: 34239158
-
Forensic drug intelligence and the rise of cryptomarkets. Part I: Studying the Australian virtual market.Forensic Sci Int. 2017 Oct;279:288-301. doi: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2017.08.026. Epub 2017 Sep 12. Forensic Sci Int. 2017. PMID: 28927690
-
Analysis of drugs in wastewater: Forensic science perspective.Forensic Sci Rev. 2023 Jul;35(2):79-105. Forensic Sci Rev. 2023. PMID: 37531496 Review.
-
Illicit drug consumption estimations derived from wastewater analysis: a critical review.Sci Total Environ. 2011 Sep 1;409(19):3564-77. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.05.030. Epub 2010 Jun 18. Sci Total Environ. 2011. PMID: 20598736 Review.
Cited by
-
Lessons learned from SARS-CoV-2 measurements in wastewater.Sci Total Environ. 2021 Dec 1;798:149177. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149177. Epub 2021 Jul 21. Sci Total Environ. 2021. PMID: 34375259 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Molecular Hydrogen on Methamphetamine-Induced Neurotoxicity and Spatial Memory Impairment.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Jul 23;10:823. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00823. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31396089 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Illicit Drug Consumption by Wastewater Analysis Using Polar Organic Chemical Integrative Sampler as a Monitoring Tool.Front Chem. 2021 Mar 30;9:596875. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.596875. eCollection 2021. Front Chem. 2021. PMID: 33859973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-throughput multi-residue quantification of contaminants of emerging concern in wastewaters enabled using direct injection liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.J Hazard Mater. 2020 Nov 5;398:122933. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122933. Epub 2020 May 24. J Hazard Mater. 2020. PMID: 32768824 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term monitoring of drug consumption patterns during the COVID-19 pandemic in a small-sized community in Brazil through wastewater-based epidemiology.Chemosphere. 2022 Sep;302:134907. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134907. Epub 2022 May 10. Chemosphere. 2022. PMID: 35561781 Free PMC article.
References
-
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC). World drug report 2017. Available from: https://www.unodc.org/wdr2017/index.html
-
- Irvine RJ, Kostakis C, Felgate PD, et al. . Population drug use in Australia: a wastewater analysis. Forensic Sci Int. 2011;210:69–73. - PubMed
-
- Lai FY, O'Brien J, Bruno R, et al. . Spatial variations in the consumption of illicit stimulant drugs across Australia: a nationwide application of wastewater-based epidemiology. Sci Total Environ. 2016;568:810–818. - PubMed
-
- Australian Criminal Intelligence Commission (ACIC) National Wastewater Drug Monitoring Program, Report 1. 2017. Available from: https://www.acic.gov.au/sites/g/files/net1491/f/national_wastewater_drug...
-
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA) Wastewater analysis and drugs – a European multi-city study. 2017. Available from: http://www.emcdda.europa.eu/topics/pods/waste-water-analysis#panel2
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

