MicroRNA-92b-5p modulates melatonin-mediated osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by targeting ICAM-1
- PMID: 31304676
- PMCID: PMC6714169
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.14490
MicroRNA-92b-5p modulates melatonin-mediated osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by targeting ICAM-1
Abstract
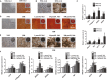
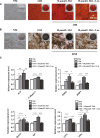
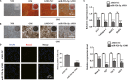
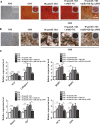
Osteoporosis is closely associated with the dysfunction of bone metabolism, which is caused by the imbalance between new bone formation and bone resorption. Osteogenic differentiation plays a vital role in maintaining the balance of bone microenvironment. The present study investigated whether melatonin participated in the osteogenic commitment of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) and further explored its underlying mechanisms. Our data showed that melatonin exhibited the capacity of regulating osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs, which was blocked by its membrane receptor inhibitor luzindole. Further study demonstrated that the expression of miR-92b-5p was up-regulated in BMSCs after administration of melatonin, and transfection of miR-92b-5p accelerated osteogenesis of BMSCs. In contrast, silence of miR-92b-5p inhibited the osteogenesis of BMSCs. The increase in osteoblast differentiation of BMSCs caused by melatonin was attenuated by miR-92b-5p AMO as well. Luciferase reporter assay, real-time qPCR analysis and western blot analysis confirmed that miR-92b-5p was involved in osteogenesis by directly targeting intracellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1). Melatonin improved the expression of miR-92b-5p, which could regulate the differentiation of BMSCs into osteoblasts by targeting ICAM-1. This study provided novel methods for treating osteoporosis.
Keywords: BMSCs; ICAM-1; MiRNA; melatonin; osteogenic differentiation; osteoporosis.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors indicate no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Ferrari SL. Osteoporosis: romosozumab to rebuild the foundations of bone strength. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2018;14:128. - PubMed
-
- Tsourdi E, Hofbauer LC. Denosumab: a new treatment option for glucocorticoid‐induced osteoporosis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018;6:428‐429. - PubMed
-
- Frontini‐López YR, Gojanovich AD, Masone D, Bustos DM, Uhart M. Adipose‐derived mesenchymal stem/stromal cells: from the lab bench to the basic concepts for clinical translation. Biocell. 2018;42(3):67‐77.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

