The plant hypersensitive response: concepts, control and consequences
- PMID: 31305008
- PMCID: PMC6640183
- DOI: 10.1111/mpp.12821
The plant hypersensitive response: concepts, control and consequences
Abstract
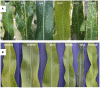
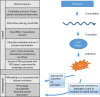
The hypersensitive defence response is found in all higher plants and is characterized by a rapid cell death at the point of pathogen ingress. It is usually associated with pathogen resistance, though, in specific situations, it may have other consequences such as pathogen susceptibility, growth retardation and, over evolutionary timescales, speciation. Due to the potentially severe costs of inappropriate activation, plants employ multiple mechanisms to suppress inappropriate activation of HR and to constrain it after activation. The ubiquity of this response among higher plants despite its costs suggests that it is an extremely effective component of the plant immune system.
Keywords: hypersensitive response.
Published 2019. This Article is a U.S. Government Work and is in the Public Domain in the USA. Molecular Plant Pathology published by British Society for Plant Pathology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hypersensitive response-related death.Plant Mol Biol. 2000 Oct;44(3):321-34. doi: 10.1023/a:1026592509060. Plant Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 11199391 Review.
-
Plant proteases in the control of the hypersensitive response.J Exp Bot. 2019 Apr 12;70(7):2087-2095. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erz030. J Exp Bot. 2019. PMID: 30715462 Review.
-
Immunity-Associated Programmed Cell Death as a Tool for the Identification of Genes Essential for Plant Innate Immunity.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1743:51-63. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7668-3_5. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29332285
-
The hypersensitive induced reaction and leucine-rich repeat proteins regulate plant cell death associated with disease and plant immunity.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2011 Jan;24(1):68-78. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-02-10-0030. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2011. PMID: 20635864
-
Preexisting systemic acquired resistance suppresses hypersensitive response-associated cell death in Arabidopsis hrl1 mutant.Plant Physiol. 2002 Apr;128(4):1234-44. doi: 10.1104/pp.010941. Plant Physiol. 2002. PMID: 11950972 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
LsGRP1, a class II glycine-rich protein of Lilium, confers plant resistance via mediating innate immune activation and inducing fungal programmed cell death.Mol Plant Pathol. 2020 Sep;21(9):1149-1166. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12968. Epub 2020 Jul 14. Mol Plant Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32662583 Free PMC article.
-
Hfq Is a Critical Modulator of Pathogenicity of Dickeya oryzae in Rice Seeds and Potato Tubers.Microorganisms. 2022 May 16;10(5):1031. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10051031. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35630473 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingolipids: A new piece in the puzzle of insect egg-triggered plant immunity.Plant Physiol. 2022 Sep 28;190(2):1088-1089. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiac350. Plant Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35880839 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Secretome analysis identified extracellular superoxide dismutase and catalase of Macrophomina phaseolina.Arch Microbiol. 2021 Dec 23;204(1):62. doi: 10.1007/s00203-021-02631-w. Arch Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34940926
-
Pseudomonas phaseolicola preferentially modulates genes encoding leucine-rich repeat and malectin domains in the bean landrace G2333.Planta. 2022 Jun 29;256(2):25. doi: 10.1007/s00425-022-03943-x. Planta. 2022. PMID: 35768557 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdul‐Baki, A.A. , Haroon, S.A. and Chitwood, D.J. (1996) Temperature effects on resistance to Meloidogyne spp. in excised tomato roots. HortScience, 31, 147–149.
-
- Alcázar, R. and Parker, J.E. (2011) The impact of temperature on balancing immune responsiveness and growth in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci. 16, 666–675. - PubMed
-
- Aust, H. (1974) The influence of temperature on infection by powdery mildew (Erysiphe graminis DC. f. sp. hordei Marchal). Z. Pflanzenkr. Pflanzenschutz, 81, 597–601.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

