Relationship between oral and gut microbiota in elderly people
- PMID: 31305026
- PMCID: PMC6688080
- DOI: 10.1002/iid3.266
Relationship between oral and gut microbiota in elderly people
Abstract
Aim: Recent studies have suggested that oral bacteria induce systemic inflammation through the alteration of gut microbiota. We examined the relationship between oral and gut microbiota to evaluate the transition of oral bacteria to the gastrointestinal tract.
Methods: Oral samples from subgingival plaque and tongue-coating and fecal samples were collected from 29 elderly subjects (age, 80.2 ± 9.1 years) and 30 adults (age, 35.9 ± 5.0 years). Genomic DNA was extracted from all samples, and DNA sequencing of bacterial 16S rRNA genes was performed for microbiota analysis. UniFrac distances were calculated to evaluate the similarity between microbial communities.
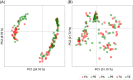
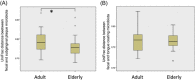
Results: Unweighted UniFrac distance indicated that the elderly group had a higher similarity between fecal and subgingival plaque microbiota than the adult group. Indeed, some bacterial taxa found in oral samples had a significantly higher prevalence in the feces of the elderly group than in that of the adult group.
Conclusions: The prevalence of oral bacterial transition to gut may be higher in the elderly than in adults, expecting that oral health care in the elderly will affect their gut microbiota composition and consequently promote human health.
Keywords: bacterial transition; elderly; fecal microbiota; oral microbiota.
© 2019 The Authors. Immunity, Inflammation and Disease Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Four of the authors, A Horigome, M Nakano, JZ Xiao, and T Odamaki, are employees of Morinaga Milk Industry. The other authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures

References
-
- Mitsuoka T, Hayakawa K. The fecal flora in man. I Composition of the fecal flora of various age groups. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1973;223:333‐342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

