Effect and safety of LCZ696 in the treatment of hypertension: A meta-analysis of 9 RCT studies
- PMID: 31305392
- PMCID: PMC6641826
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016093
Effect and safety of LCZ696 in the treatment of hypertension: A meta-analysis of 9 RCT studies
Abstract
Background: LCZ696 has been introduced in patients with hypertension in several trials. Here, we performed a meta-analysis to evaluate the effect and safety of LCZ696 in hypertensive patients.
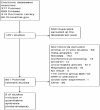
Methods: PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane Library and ClinicalTrials.gov databases were searched to identify the available randomized controlled trials (RCTs) investigating the effect and safety of LCZ696 in hypertension patients. The last search date was October 31, 2018.
Results: Nine RCTs with 6765 subjects were finally included, in which 8 trials compared the effect and safety between LCZ696 and angiotensin receptor antagonists (ARBs). Evidences showed LCZ696, compared with ARBs, achieved a better blood pressure control rate (OR 1.24, 95% CI: 1.14-1.35), specifically, LCZ696 were better at reducing systolic blood pressure [WMD -4.11 mmHg, 95% CI: (-5.13, -3.08) mmHg], diastolic blood pressure [WMD -1.79 mmHg, 95% CI: (-2.22, -1.37) mmHg], mean 24-hour ambulatory systolic blood pressure [WMD -3.24 mmHg, 95% CI: (-4.48, -1.99) mmHg] and mean 24-hour ambulatory diastolic blood pressure [WMD -1.25 mmHg, 95% CI: (-1.81, -0.69) mmHg]. There was no difference in the events of adverse events (risk ratio [RR] 1.01, 95% CI: 0.39-1.09), serious adverse events (RR 0.80, 95% CI: 0.52-1.22) and discontinuation of treatment for any adverse events (RR 0.79, 95% CI: 0.56-1.11) between LCZ696 group and ARB/placebo group, except LCZ696 reduced the rate of headaches (RR 0.69, 95% CI: 0.48-0.99) while increased cough (RR 2.12, 95% CI: 1.11-4.04; P = .02; I = 25%).
Conclusion: Our finding provides evidence that LCZ 696 was more effective than ARB on blood pressure control and was safe enough in patients with hypertension.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this article
Figures





Similar articles
-
The Effects of LCZ696 in Patients With Hypertension Compared With Angiotensin Receptor Blockers: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2017 Sep;22(5):447-457. doi: 10.1177/1074248417693379. Epub 2017 Mar 2. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28793821
-
Efficacy and Safety Comparative of Sacubitril/Valsartan vs. Olmesartan in the Treatment of hypertension: A Meta-analysis of RCTs.Am J Hypertens. 2023 Nov 15;36(12):643-650. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpad075. Am J Hypertens. 2023. PMID: 37596996
-
Efficacy and Safety of LCZ696 for Short-term Management of Essential Hypertension Compared With ARBs: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2021 May 1;77(5):650-659. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000001001. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33951700
-
Efficacy and safety of sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696) add-on to amlodipine in Asian patients with systolic hypertension uncontrolled with amlodipine monotherapy.J Hypertens. 2017 Apr;35(4):877-885. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000001219. J Hypertens. 2017. PMID: 28030431 Clinical Trial.
-
Antihypertensive effect of sacubitril/valsartan: a meta-analysis.Minerva Cardioangiol. 2019 Jun;67(3):214-222. doi: 10.23736/S0026-4725.19.04869-2. Epub 2019 Mar 18. Minerva Cardioangiol. 2019. Retraction in: Minerva Cardiol Angiol. 2023 Oct;71(5):609. doi: 10.23736/S2724-5683.23.06420-7. PMID: 30895762 Retracted. Review.
Cited by
-
Angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitors for hypertension-hemodynamic effects and relevance to hypertensive heart disease.Hypertens Res. 2022 Jul;45(7):1097-1110. doi: 10.1038/s41440-022-00923-2. Epub 2022 May 2. Hypertens Res. 2022. PMID: 35501475 Review.
-
Sacubitril/Valsartan for Blood Pressure Lowering in Non-Dialysis-Dependent Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 3-5 Patients With Hypertension: A Multicenter Clinical Study.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2025 Jan;27(1):e14969. doi: 10.1111/jch.14969. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2025. PMID: 39826131 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and Efficiency of Non-drug Therapy Among Community-Dwelling Adults With Hypertension in China: A Protocol for Network Meta-Analysis and Cost-Effectiveness Analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Feb 25;8:651559. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.651559. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33718415 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Antihypertensive Medications to Target the Renin-Angiotensin System: Mechanisms and Research.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Apr 21;26(4):27963. doi: 10.31083/RCM27963. eCollection 2025 Apr. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40351692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitors: Comprehensive review and implications in hypertension treatment.Hypertens Res. 2021 Oct;44(10):1239-1250. doi: 10.1038/s41440-021-00706-1. Epub 2021 Jul 21. Hypertens Res. 2021. PMID: 34290389 Review.
References
-
- Kjeldsen SE. Hypertension and cardiovascular risk: general aspects. Pharmacol Res 2018;129:95–9. - PubMed
-
- Vardeny O, Claggett B, Kachadourian J, et al. Incidence, predictors, and outcomes associated with hypotensive episodes among heart failure patients receiving sacubitril/valsartan or enalapril: the PARADIGM-HF trial (prospective comparison of angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor to determine impact on global mortality and morbidity in heart failure). Circ Heart Fail 2018;11:e004745. - PubMed
-
- De Vecchis R, Ariano C, Di Biase G, et al. Sacubitril/valsartan for heart failure with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction: a retrospective cohort study. Herz 2018. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

