Lupus intestinal pseudo-obstruction and hydronephrosis: Case report
- PMID: 31305400
- PMCID: PMC6641825
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016178
Lupus intestinal pseudo-obstruction and hydronephrosis: Case report
Abstract
Introduction: Intestinal pseudo-obstruction (IPO) is a rare and life-threatening complication of lupus.
Patient concerns: A patient with long-standing lupus developed recurrent abdominal pain and distension as well as nausea and emesis.
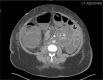
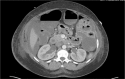
Diagnosis: Imaging showed dilated small bowel loops with air-fluid levels and bowel wall thickening. She also had bilateral hydronephrosis.
Interventions: She was given high-doses of intravenous steroids and cyclophosphamide.
Outcomes: Her symptoms resolved within a week of starting immunosuppression. She was eventually transitioned to mycophenolate mofetil. She remained in remission and immunosuppression was successfully stopped after 1 year.
Conclusions: Intestinal pseudo-obstruction is a rare complication of lupus that is often seen in association with ureterohydronephrosis and interstitial cystitis. This clinical syndrome is thought to be because of smooth muscle dysmotility of the gastrointestinal and genitourinary tracts, although the exact mechanism of dysmotility remains unknown. This condition is often responsive to immunosuppression if recognized and treated promptly.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intestinal pseudo-obstruction and ureterohydronephrosis as the presenting manifestations of relapse in a lupus patient.Lupus. 2004;13(12):954-6. doi: 10.1191/0961203304u1064cr. Lupus. 2004. PMID: 15645752
-
Tacrolimus treatment for refractory lupus cystitis.Mod Rheumatol. 2006;16(4):264-6. doi: 10.1007/s10165-006-0494-2. Mod Rheumatol. 2006. PMID: 16906381
-
Intestinal pseudo-obstruction in systemic lupus erythematosus: an uncommon but important clinical manifestation.Lupus. 2000;9(1):11-8. doi: 10.1177/096120330000900104. Lupus. 2000. PMID: 10713642 Review.
-
Clinical analysis of 61 systemic lupus erythematosus patients with intestinal pseudo-obstruction and/or ureterohydronephrosis: a retrospective observational study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2015 Jan;94(4):e419. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000419. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015. PMID: 25634172 Free PMC article.
-
Visceral muscle dysmotility syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus: case report and review of the literature.Rheumatol Int. 2012 Jun;32(6):1701-3. doi: 10.1007/s00296-011-1856-4. Epub 2011 Mar 24. Rheumatol Int. 2012. PMID: 21431943 Review.
Cited by
-
An Atypical Initial Manifestation of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Lupus Enteritis Accompanied by Intestinal Pseudo-Obstruction and Bilateral Hydronephroureter.Cureus. 2023 Dec 16;15(12):e50628. doi: 10.7759/cureus.50628. eCollection 2023 Dec. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38226118 Free PMC article.
-
Immune-related ureteritis and cystitis induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors: Case report and literature review.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 6;13:1051577. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1051577. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36685488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lupus cystitis: unusual cause of renal failure in systemic lupus erythematosus.BMJ Case Rep. 2019 Dec 19;12(12):e233446. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2019-233446. BMJ Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 31862817 Free PMC article.
-
Very Severe and Refractory Noninfectious Cystitis in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Potential Role of Rituximab Therapy.Case Rep Rheumatol. 2021 Feb 27;2021:6610111. doi: 10.1155/2021/6610111. eCollection 2021. Case Rep Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 33728086 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nguyen H, Khanna N. Intestinal pseudo-obstruction as a presenting manifestation of systemic lupus erythematosus: case report and review of the literature. South Med J 2004;97:186–9. - PubMed
-
- Zhang L, Xu D, Yang H, et al. Clinical features, morbidity, and risk factors of intestinal pseudo-obstruction in systemic lupus erythematosus: a retrospective case-control study. J Rheumatol 2016;43:559–64. - PubMed
-
- Yuan S, Lian F, Chen D, et al. Clinical features and associated factors of abdominal pain in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 2013;40:2015–22. - PubMed
-
- Alexopoulou A, Andrianakos A, Dourakis SP. Intestinal pseudo-obstruction and ureterohydronephrosis as the presenting manifestations of relapse in a lupus patient. Lupus 2004;13:954–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical