The risk of end-stage renal disease in systemic lupus erythematosus: A nationwide population-based study in Korea
- PMID: 31305460
- PMCID: PMC6641670
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016420
The risk of end-stage renal disease in systemic lupus erythematosus: A nationwide population-based study in Korea
Abstract
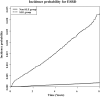
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is known to be one of the leading causes of end-stage renal disease (ESRD). The aim of this study was to estimate the incidence rate of ESRD and the risk for progression to ESRD in SLE patients compared to the general population.A total of 21,253 SLE patients were extracted from the Korean National Health Insurance Service database between 2008 and 2013. Age-and sex-matched controls (n = 106,265) were randomly sampled in a 5:1 ratio from non-SLE individuals. Both cohorts were followed up for development of ESRD until 2015.During the median 7.53 years of follow-up, 533 (2.51%) cases of ESRD were newly developed in SLE patients and 145 (0.14%) cases in matched controls (incidence rate: 4.075 and 0.219 per 1000 person-year, respectively). SLE patients were at higher risk for ESRD development compared to matched controls (hazard ratio [HR], 9.84; 95% confidence interval [CI] 8.10-11.96) after multivariate adjustment. In subgroup analysis, the risk for ESRD was higher in male (HR, 7.76; 95% CI 5.07-11.90) and female patients with SLE (HR, 10.48; 95% CI 8.41-13.07) than in matched controls. When analyzed by age group, the younger the age, the higher the risk of ESRD versus non-SLE matched controls; this result was also significant after adjustment. In subgroup analysis according to comorbidities, the SLE group had a significantly higher risk of ESRD than the non-SLE group in almost all subgroups.SLE was associated with an increased incidence of ESRD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Risk of end-stage renal disease in systemic lupus erythematosus patients: a nationwide population-based study.Int J Rheum Dis. 2016 Nov;19(11):1175-1182. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.12828. Epub 2016 Feb 10. Int J Rheum Dis. 2016. PMID: 26864331
-
Incidence of progression from newly diagnosed systemic lupus erythematosus to end stage renal disease and all-cause mortality: a nationwide cohort study in Taiwan.Int J Rheum Dis. 2013 Dec;16(6):747-53. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.12208. Epub 2013 Nov 4. Int J Rheum Dis. 2013. PMID: 24382283
-
Infection-related hospitalization and risk of end-stage renal disease in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a nationwide population-based study.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2017 Oct 1;32(10):1683-1690. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfw407. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2017. PMID: 28011646
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus, lupus nephritis and end-stage renal disease: a pragmatic review mapping disease severity and progression.Lupus. 2020 Aug;29(9):1011-1020. doi: 10.1177/0961203320932219. Epub 2020 Jun 22. Lupus. 2020. PMID: 32571142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prostate cancer in systemic lupus erythematosus.Int J Cancer. 2011 Dec 15;129(12):2966-9. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25956. Epub 2011 Mar 29. Int J Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21448902 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Smoking and risk of incident end-stage kidney disease in general population: A Nationwide Population-based Cohort Study from Korea.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 20;9(1):19511. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56113-7. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31862942 Free PMC article.
-
Dose adjustment of rheumatology and allergy/immunology medications in chronic kidney disease: awareness and knowledge among internal medicine housestaff.Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2023 Jul 18;36(5):627-634. doi: 10.1080/08998280.2023.2228172. eCollection 2023. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2023. PMID: 37663380 Free PMC article.
-
Multidisciplinary Lupus Nephritis Clinic Reduces Time to Renal Biopsy and Improves Care Quality.ACR Open Rheumatol. 2022 Jul;4(7):581-586. doi: 10.1002/acr2.11435. Epub 2022 Apr 8. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 35396828 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and outcomes of end-stage kidney disease in patients with systemic lupus erythematous: a population-based study.Rheumatol Int. 2024 Mar;44(3):469-475. doi: 10.1007/s00296-023-05409-z. Epub 2023 Aug 14. Rheumatol Int. 2024. PMID: 37580433 Free PMC article.
-
Non-traditional risk factors of progression of chronic kidney disease in adult population: a scoping review.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Jun 2;10:1193984. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1193984. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37332753 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Croca SC, Rodrigues T, Isenberg DA. Assessment of a lupus nephritis cohort over a 30-year period. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2011;50:1424–30. - PubMed
-
- Maroz N, Segal MS. Lupus nephritis and end-stage kidney disease. Am J Med Sci 2013;346:319–23. - PubMed
-
- Crosslin KL, Wiginton KL. The impact of race and ethnicity on disease severity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ethn Dis 2009;19:301–7. - PubMed
-
- Jakes RW, Bae SC, Louthrenoo W, et al. Systematic review of the epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus in the Asia-Pacific region: prevalence, incidence, clinical features, and mortality. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2012;64:159–68. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

