Effects of Amylin Against Amyloid-β-Induced Tauopathy and Synapse Loss in Primary Neurons
- PMID: 31306122
- PMCID: PMC6833957
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-190161
Effects of Amylin Against Amyloid-β-Induced Tauopathy and Synapse Loss in Primary Neurons
Abstract
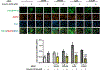
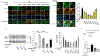
Recent studies demonstrate that peripheral amylin treatment reduces pathology in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, soluble and aggregated amylin are distinct species; while amylin is a physiological neuropeptide, amylin aggregation is a pathological factor for diabetes. We thus hypothesized that because of their similarity in secondary structures, amylin antagonizes amyloid-β peptide (Aβ)-induced AD pathology in neurons with a dose-dependent pattern. To test the hypothesis, we conducted both in vitro and in vivo experiments with different doses of amylin and with its analog, pramlintide. Here we report that a high concentration of either Aβ or amylin alone induced tau phosphorylation (pTau) in primary neurons. Interestingly, with a low concentration, amylin had direct effects to reverse the Aβ-induced pTau, as well as damaged neuronal synapses and neurite disorganization. However, when the concentration was high (10.24 μM), amylin lost the effects against the Aβ-induced cellular AD pathology and, together with Aβ, worsened tauopathy in neurons. In the 5XFAD AD mouse model, daily peripheral amylin treatment with a low dose (200 μg/kg) more effectively reduced amyloid burden, and increased synapse, but with a high dose (800 μg/kg), it more effectively reduced tauopathy. Correspondingly, amylin treatment improved learning and memory in these mice. It demonstrates that amylin has a dose-dependent U-shape effect against AD pathogenesis. Within a physiological range, amylin is a neuroprotective hormone against AD in neurons; but when both Aβ and amylin concentrations are elevated, imbalance of Aβ and amylin may contribute to brain AD pathogenesis.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; U-shape; amylin; amyloid-β peptide; pramlintide; synapse; tauopathy.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Pramlintide Antagonizes Beta Amyloid (Aβ)- and Human Amylin-Induced Depression of Hippocampal Long-Term Potentiation.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Jan;54(1):748-754. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-9684-x. Epub 2016 Jan 15. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 26768593
-
Intraperitoneal injection of the pancreatic peptide amylin potently reduces behavioral impairment and brain amyloid pathology in murine models of Alzheimer's disease.Mol Psychiatry. 2015 Feb;20(2):252-62. doi: 10.1038/mp.2014.17. Epub 2014 Mar 11. Mol Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 24614496 Free PMC article.
-
Amylin receptor ligands reduce the pathological cascade of Alzheimer's disease.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Jun;119:170-181. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.03.030. Epub 2017 Mar 28. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28363773 Free PMC article.
-
Amylin and its G-protein-coupled receptor: A probable pathological process and drug target for Alzheimer's disease.Neuroscience. 2017 Jul 25;356:44-51. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.05.024. Epub 2017 May 19. Neuroscience. 2017. PMID: 28528968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amylin Pharmacology in Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis and Treatment.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022;20(10):1894-1907. doi: 10.2174/1570159X19666211201093147. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34852745 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Amylin exacerbates tau pathology in the visual cortex of diabetic mice by impairing lysosomal activity.Genes Dis. 2025 Mar 18;12(5):101602. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2025.101602. eCollection 2025 Sep. Genes Dis. 2025. PMID: 40605977 Free PMC article.
-
PPARs and Their Neuroprotective Effects in Parkinson's Disease: A Novel Therapeutic Approach in α-Synucleinopathy?Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 7;24(4):3264. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043264. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Molecular Clock and Neurodegenerative Disease: A Stressful Time.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Mar 26;8:644747. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.644747. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33889597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of Plasma Amylin Concentration With Alzheimer Disease and Brain Structure in Older Adults.JAMA Netw Open. 2019 Aug 2;2(8):e199826. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.9826. JAMA Netw Open. 2019. PMID: 31433485 Free PMC article.
-
Varicella-Zoster Virus Infection of Primary Human Spinal Astrocytes Produces Intracellular Amylin, Amyloid-β, and an Amyloidogenic Extracellular Environment.J Infect Dis. 2020 Mar 16;221(7):1088-1097. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiz560. J Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 31665341 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nishi M, Sanke T, Seino S, Eddy RL, Fan YS, Byers MG, Shows TB, Bell GI, Steiner DF (1989) Human islet amyloid polypeptide gene: complete nucleotide sequence, chromosomal localization, and evolutionary history. Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 3, 1775–1781. - PubMed
-
- Lutz TA (2013) The interaction of amylin with other hormones in the control of eating. Diabetes, obesity & metabolism 15, 99–111. - PubMed
-
- Adler BL, Yarchoan M, Hwang HM, Louneva N, Blair JA, Palm R, Smith MA, Lee HG, Arnold SE, Casadesus G (2014) Neuroprotective effects of the amylin analogue pramlintide on Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis and cognition. Neurobiol Aging 35, 793–801. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K23 AG022476/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG059424/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG059805/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG049899/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG050471/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG017485/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS089544/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AG050842/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG059925/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG061706/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013846/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG064932/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG056318/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG045757/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

