Crystal structure of the N domain of Lon protease from Mycobacterium avium complex
- PMID: 31306520
- PMCID: PMC6699098
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.3687
Crystal structure of the N domain of Lon protease from Mycobacterium avium complex
Abstract
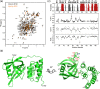
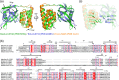
Lon protease is evolutionarily conserved in prokaryotes and eukaryotic organelles. The primary function of Lon is to selectively degrade abnormal and certain regulatory proteins to maintain the homeostasis in vivo. Lon mainly consists of three functional domains and the N-terminal domain is required for the substrate selection and recognition. However, the precise contribution of the N-terminal domain remains elusive. Here, we determined the crystal structure of the N-terminal 192-residue construct of Lon protease from Mycobacterium avium complex at 2.4 å resolution,and measured NMR-relaxation parameters of backbones. This structure consists of two subdomains, the β-strand rich N-terminal subdomain and the five-helix bundle of C-terminal subdomain, connected by a flexible linker,and is similar to the overall structure of the N domain of Escherichia coli Lon even though their sequence identity is only 26%. The obtained NMR-relaxation parameters reveal two stabilized loops involved in the structural packing of the compact N domain and a turn structure formation. The performed homology comparison suggests that structural and sequence variations in the N domain may be closely related to the substrate selectivity of Lon variants. Our results provide the structure and dynamics characterization of a new Lon N domain, and will help to define the precise contribution of the Lon N-terminal domain to the substrate recognition.
Keywords: Mycobacterium avium complex; Lon protease; backbone dynamics; crystal structure; the N domain.
© 2019 The Protein Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Crystal structures of Bacillus subtilis Lon protease.J Mol Biol. 2010 Aug 27;401(4):653-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.06.030. Epub 2010 Jun 19. J Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20600124
-
Crystal structure of XCC3289 from Xanthomonas campestris: homology with the N-terminal substrate-binding domain of Lon peptidase.Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2020 Oct 1;76(Pt 10):488-494. doi: 10.1107/S2053230X20011875. Epub 2020 Sep 16. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2020. PMID: 33006577 Free PMC article.
-
The N-terminal substrate-recognition domain of a LonC protease exhibits structural and functional similarity to cytosolic chaperones.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2013 Sep;69(Pt 9):1789-97. doi: 10.1107/S090744491301500X. Epub 2013 Aug 17. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2013. PMID: 23999302
-
Crystal structure of the AAA+ alpha domain of E. coli Lon protease at 1.9A resolution.J Struct Biol. 2004 Apr-May;146(1-2):113-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2003.09.003. J Struct Biol. 2004. PMID: 15037242 Review.
-
Slicing a protease: structural features of the ATP-dependent Lon proteases gleaned from investigations of isolated domains.Protein Sci. 2006 Aug;15(8):1815-28. doi: 10.1110/ps.052069306. Protein Sci. 2006. PMID: 16877706 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Study on molecular response of alfalfa to low temperature stress based on transcriptomic analysis.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Dec 23;24(1):1244. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05987-5. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 39716071 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular insights into substrate recognition and discrimination by the N-terminal domain of Lon AAA+ protease.Elife. 2021 Apr 30;10:e64056. doi: 10.7554/eLife.64056. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33929321 Free PMC article.
-
Complete three-dimensional structures of the Lon protease translocating a protein substrate.Sci Adv. 2021 Oct 15;7(42):eabj7835. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abj7835. Epub 2021 Oct 15. Sci Adv. 2021. PMID: 34652947 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and the Mode of Activity of Lon Proteases from Diverse Organisms.J Mol Biol. 2022 Apr 15;434(7):167504. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2022.167504. Epub 2022 Feb 17. J Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35183556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural basis for the allosteric activation of Lon by the heat shock protein LarA.Nat Commun. 2025 Mar 5;16(1):2212. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-57482-6. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40044692 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lande L, George J, Plush T. Mycobacterium avium complex pulmonary disease: new epidemiology and management concepts. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2018;31:199–207. - PubMed
-
- Griffith DE, Aksamit T, Brown‐Elliott BA, et al. An official ATS/IDSA statement: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of nontuberculous mycobacterial diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175:367–416. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

