Prophylactic simvastatin treatment modulates the immune response and increases survival of mice following induction of lethal sepsis
- PMID: 31307265
- PMCID: PMC6726777
- DOI: 10.1177/0300060519858508
Prophylactic simvastatin treatment modulates the immune response and increases survival of mice following induction of lethal sepsis
Retraction in
-
Retraction Notice.J Int Med Res. 2024 Jan;52(1):3000605241228165. doi: 10.1177/03000605241228165. J Int Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38217421 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objective: To investigate whether and how simvastatin mediates protection from lethal sepsis, using a mouse model.
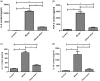
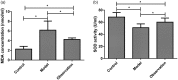
Methods: Sixty C57BL/6 mice were selected and divided into three groups (“control,” “model,” and “observation”; n = 20 mice per group). Mice in the model and observation groups underwent cecal ligation and puncture; mice in the observation group received simvastatin. After 24 hours of induced sepsis, serum concentrations of IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1, and IL-10 were measured by ELISA. Serum malondialdehyde (MDA) concentrations and serum superoxide dismutase (SOD) activities were quantified by radioimmunoassay.
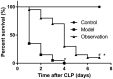
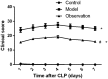
Results: The mean duration of survival of mice in the observation group was significantly longer than that of the model group. The serum concentrations of IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1, IL-10, and MDA were significantly higher in the observation group than in the control group. Serum SOD activities were significantly lower in the observation group than in the control group.
Conclusions: Simvastatin can alleviate symptoms of sepsis in mice and improve their rates of survival. The mechanism of action of simvastatin may be mediated by inhibition of the systemic inflammatory response and oxidative stress.
Keywords: Sepsis; cecal ligation and puncture; interleukin-1; interleukin-10; interleukin-6; malondialdehyde; oxidative stress; simvastatin; superoxide dismutase; survival rate.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Simvastatin protects against T cell immune dysfunction in abdominal sepsis.Shock. 2012 Nov;38(5):524-31. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e31826fb073. Shock. 2012. PMID: 23042198
-
Prophylactic Treatment With Simvastatin Modulates the Immune Response and Increases Animal Survival Following Lethal Sepsis Infection.Front Immunol. 2018 Sep 21;9:2137. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02137. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30298072 Free PMC article.
-
Old Mice Demonstrate Organ Dysfunction as well as Prolonged Inflammation, Immunosuppression, and Weight Loss in a Modified Surgical Sepsis Model.Crit Care Med. 2019 Nov;47(11):e919-e929. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000003926. Crit Care Med. 2019. PMID: 31389840 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Simvastatin on the Intestinal Rho/ROCK Signaling Pathway in Rats With Sepsis.J Surg Res. 2018 Dec;232:531-538. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2018.07.016. Epub 2018 Aug 3. J Surg Res. 2018. PMID: 30463769
-
Impaired cell-mediated immunity in experimental abdominal sepsis and the effect of interleukin 2.Arch Surg. 1992 Jul;127(7):859-63. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1992.01420070123022. Arch Surg. 1992. PMID: 1524487
References
-
- Perl M, Chung CS, Garber M, et al. Contribution of anti-inflammatory/immune suppressive processes to the pathology of sepsis. Front Biosci 2006: 11: 272–299. - PubMed
-
- Simmons MD, Daniel S, Temple M. Sepsis programme successes are responsible for the increased detection of bacteraemia. J Hosp Infect 2019: 101: 93–99. - PubMed
-
- Lee WL. Immunotherapy for sepsis: a good idea or another dead end? Anesthesiology 2018; 129: 5–7. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000002237 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

