Prognostic value of TGF-β in lung cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 31307405
- PMCID: PMC6631541
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-019-5917-5
Prognostic value of TGF-β in lung cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Lung cancer is the most important cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide and the overall survival of patients with non-small cell lung cancer has not improved. Transforming growth factor beta or TGF-β is a polypeptide member of the transforming growth factor beta superfamily of cytokines, while far fewer clinical studies addressing the association between TGF-β expression and the disease prognosis have been reported up to now. Therefore, our meta-analysis aims to determine the prognostic significance of TGF-β expression in lung cancer patients.
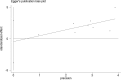
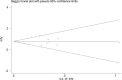
Methods: PubMed, EMBASE, the Web of Science and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) databases were searched for full-text literature citations. We applied the hazard ratio (HR) with 95% confidence interval (CI) as the appropriate summarized statistics. Q-test and I2 statistic were used to estimate the level of heterogeneity. The publication bias was detected by Begg's test and Egger's test.
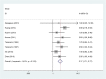
Results: Eight eligible studies involving 579 patients were selected for this meta-analysis. The combined HR for the eight eligible studies was 2.17 (95% CI: 1.71-2.77, P < 0.00001) and heterogeneity of overall prognosis was relatively low (I2 = 14.2%, P = 0.319). We further undertook the subgroup analysis including assessment of the association between TGF-β expression and pathology of the lung cancer, treatment and quantity of sample in studies. All the results revealed that a significantly high TGF-β expression in patients was an indicator of poor survival. Neither Begg's test nor Egger's test found publication bias in any analysis.
Conclusions: The present evidence indicates that TGF-β expression can significantly predict the worse prognosis in patients with lung cancer. The findings of our meta-analysis may be confirmed in the future by the use of more updated review pooling and additional relevant investigations.
Keywords: Lung cancer; Meta-analysis; Prognosis; TGF-β.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prognostic value of let-7 in lung cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis.Transl Cancer Res. 2020 Oct;9(10):6354-6361. doi: 10.21037/tcr-20-1240. Transl Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 35117243 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of stromal decorin expression in patients with breast cancer: a meta-analysis.J Thorac Dis. 2015 Nov;7(11):1939-50. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2015.11.29. J Thorac Dis. 2015. PMID: 26716032 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Impact of Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-1 in Non- Small Cell Lung Cancer: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Curr Med Chem. 2019;26(42):7694-7713. doi: 10.2174/0929867325666180904114455. Curr Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30182835
-
Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of thyroid transcription factor-1 expression in small cell lung cancer: A systemic review and meta-analysis.Pathol Res Pract. 2019 Dec;215(12):152706. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2019.152706. Epub 2019 Oct 24. Pathol Res Pract. 2019. PMID: 31704153
-
Podoplanin is a useful prognostic marker and indicates better differentiation in lung squamous cell cancer patients? A systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2020 May 14;20(1):424. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-06936-9. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32408907 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Regulation of TGF-β1-Induced EMT by Autophagy-Dependent Energy Metabolism in Cancer Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 4;14(19):4845. doi: 10.3390/cancers14194845. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36230768 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of differentially expressed genes in non-small cell lung cancer.Aging (Albany NY). 2019 Dec 9;11(23):11170-11185. doi: 10.18632/aging.102521. Epub 2019 Dec 9. Aging (Albany NY). 2019. PMID: 31816603 Free PMC article.
-
Lung Cancer Induces NK Cell Contractility and Cytotoxicity Through Transcription Factor Nuclear Localization.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 May 16;10:871326. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.871326. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35652099 Free PMC article.
-
Reducing tumor invasiveness by ramucirumab and TGF-β receptor kinase inhibitor in a diffuse-type gastric cancer patient-derived cell model.Cancer Med. 2021 Oct;10(20):7253-7262. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4259. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 34542244 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting immunosuppression by TGF-β1 for cancer immunotherapy.Biochem Pharmacol. 2021 Oct;192:114697. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114697. Epub 2021 Jul 22. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34302795 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dvornikov D, Schneider MA, Ohse S, Szczygiel M, Titkova I, Rosenblatt M, Muley T, Warth A, Herth FJ, Dienemann H et al: Expression ratio of the TGF beta-inducible gene MYO10 is prognostic for overall survival of squamous cell lung cancer patients and predicts chemotherapy response. 2018, 8(1):9517. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Deng G, Chen L, Zhang Y, Fan S, Li W, Lu J, Chen X. Fucosyltransferase 2 induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition via TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway in lung adenocarcinaoma. Exp Cell Res. 2018. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

