Impact of uPA/PAI-1 and disseminated cytokeratin-positive cells in breast cancer
- PMID: 31307406
- PMCID: PMC6632216
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-019-5857-0
Impact of uPA/PAI-1 and disseminated cytokeratin-positive cells in breast cancer
Abstract
Background: The protease uPA and its inhibitor PAI-1 play major roles in hemostasis and are also involved in cancer progression. This is mainly caused by their ability to degrade extracellular matrix-facilitating tumor cell migration. This study aimed to investigate the impact of uPA/PAI-1 and disseminated cytokeratin-positive cells (dCK+) on the outcome and the existence of synergistic effects.
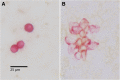
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed a cohort of 480 breast cancer cases with known uPA/PAI-1 and dCK+ status. uPA/PAI-1 was tested on fresh tumor samples using a commercial ELISA test. Bone marrow aspirates were investigated immunocytochemically for CK18.
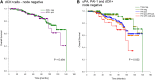
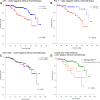
Results: DCK+ cells were identified in 23% of cases. uPA positivity was significantly associated with the occurrence of dCK+ cells (P = 0.028). uPA and PAI-1 were significantly associated with outcome in the subgroup of early-stage cases without chemotherapy. DCK+ cells alone were not prognostic. However, we found synergistic effects. In the subgroup of node-negative cases with and without chemotherapy, the prognostic impact of uPA and PAI-1 was enhanced in cases with additional dCK-positivity (triple +). In cases without chemotherapy, triple-positive status was independently prognostic (HR: 9.3 CI: 1.1-75) next to T stage.
Conclusions: uPA and PAI-1 seem to influence the metastatic potential of dCK+ cells, which underlines its important role in tumor progression.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Circulating tumor cells; Prognosis; Proteases.
Conflict of interest statement
B. Märkl received free femtelle™ test kits from the American Diagnostica GmbH and Sekisui Diagnostics GmbH for previous studies. All other authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical value of extended biologic staging by bone marrow micrometastases and tumor-associated proteases in gastric cancer.Ann Surg. 1997 Dec;226(6):736-44; discussion 744-5. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199712000-00010. Ann Surg. 1997. PMID: 9409572 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor stroma is the predominant uPA-, uPAR-, PAI-1-expressing tissue in human breast cancer: prognostic impact.Histol Histopathol. 2009 Jul;24(7):869-77. doi: 10.14670/HH-24.869. Histol Histopathol. 2009. PMID: 19475533
-
Impact of guideline-based use of uPA/PAI-1 on patient outcome in intermediate-risk early breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016 Jan;155(1):109-15. doi: 10.1007/s10549-015-3653-3. Epub 2015 Dec 7. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016. PMID: 26643086
-
uPA and PAI-1 as biomarkers in breast cancer: validated for clinical use in level-of-evidence-1 studies.Breast Cancer Res. 2014 Aug 22;16(4):428. doi: 10.1186/s13058-014-0428-4. Breast Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25677449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) and its inhibitor PAI-I: novel tumor-derived factors with a high prognostic and predictive impact in breast cancer.Thromb Haemost. 2004 Mar;91(3):450-6. doi: 10.1160/TH03-12-0798. Thromb Haemost. 2004. PMID: 14983219 Review.
Cited by
-
Biomarkers in Breast Cancer: An Old Story with a New End.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jun 28;14(7):1364. doi: 10.3390/genes14071364. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37510269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global Increase in Breast Cancer Incidence: Risk Factors and Preventive Measures.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Apr 18;2022:9605439. doi: 10.1155/2022/9605439. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. Retraction in: Biomed Res Int. 2023 Dec 29;2023:9872034. doi: 10.1155/2023/9872034. PMID: 35480139 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
-
A cross-sectional study on the expression of fibrinolytic system components and metalloproteinase-9 in women with early-stage and metastases breast cancer in Tucumán, Argentina.Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2025 Apr 18;23:eAO1237. doi: 10.31744/einstein_journal/2025AO1237. eCollection 2025. Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2025. PMID: 40266038 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-cancer potential of casein and its derivatives: novel strategies for cancer treatment.Med Oncol. 2024 Jul 11;41(8):200. doi: 10.1007/s12032-024-02403-8. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38990440 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Immunohistochemical Markers for Pleural Mesothelioma Subtyping.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Sep 14;13(18):2945. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13182945. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37761312 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Krebs in Deutschland für 2013/2014. Berlin; 2017.
-
- Nicolini A, Ferrari P, Duffy MJ. Prognostic and predictive biomarkers in breast cancer: past, present and future. Semin Cancer Biol. 2017. - PubMed
-
- Denkert C, Loibl S, Noske A, Roller M, Muller BM, Komor M, Budczies J, Darb-Esfahani S, Kronenwett R, Hanusch C, et al. Tumor-associated lymphocytes as an independent predictor of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(1):105–113. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.23.7370. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

