Macrophage-derived exosomal microRNA-501-3p promotes progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma through the TGFBR3-mediated TGF-β signaling pathway
- PMID: 31307515
- PMCID: PMC6631643
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-019-1313-x
Macrophage-derived exosomal microRNA-501-3p promotes progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma through the TGFBR3-mediated TGF-β signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: Exosomes from cancer cells or immune cells, carrying bio-macromolecules or microRNAs (miRNAs), participate in tumor pathogenesis and progression by modulating microenvironment. Our study aims to investigate the role of these microRNA-501-3p (miR-501-3p) containing exosomes derived from tumor-associated macrophage (TAM) in the progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC).
Methods: Firstly, the function of TAM recruitment in PDAC tissues was assessed, followed by identification of the effects of M2 macrophage-derived exosomes on PDAC cell activities and tumor formation and metastasis in mice. In silico analysis was conducted to predict differentially expressed genes and regulatory miRNAs related to PDAC treated with macrophages, which determined miR-501-3p and TGFBR3 for subsequent experiments. Next, gain- and loss-of-function experiments were performed to examine their role in PDAC progression with the involvement of the TGF-β signaling pathway.
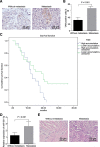
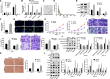
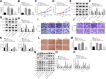
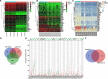
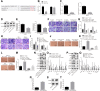
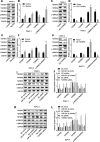
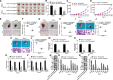
Results: TAM recruitment in PDAC tissues was associated with metastasis. Highly expressed miR-501-3p was observed in PDAC tissues and TAM-derived exosomes. Both M2 macrophage-derived exosomes and miR-501-3p promoted PDAC cell migration and invasion, as well as tumor formation and metastasis in nude mice. MiR-501-3p was verified to target TGFBR3. PDAC cells presented with down-regulated TGFBR3, which was further decreased in response to M2 macrophage treatment. TGF-β signaling pathway activation was implicated in the promotion of miR-501-3p in PDAC development. The suppression of macrophage-derived exosomal miR-501-3p resulted in the inhibition of tumor formation and metastasis in vivo.
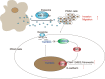
Conclusion: M2 macrophage-derived exosomal miR-501-3p inhibits tumor suppressor TGFBR3 gene and facilitates the development of PDAC by activating the TGF-β signaling pathway, which provides novel targets for the molecular treatment of PDAC.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Cell invasion; Exosome; M2 macrophage; Metastasis; MicroRNA-501-3p; Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; TGF-β signaling pathway; TGFBR3.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-323-3p inhibits cell invasion and metastasis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma via direct suppression of SMAD2 and SMAD3.Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 22;7(12):14912-24. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7482. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26908446 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal miR-199a-3p Secreted From Cancer-Associated Adipocytes Promotes Pancreatic Cancer Progression.Cancer Med. 2024 Oct;13(20):e70265. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70265. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 39431622 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer-associated fibroblast-derived exosome Leptin promotes malignant biological lineage in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by regulating ABL2 via miR-224-3p.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Sep 19;51(1):995. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09928-1. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39298063 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: MicroRNAs Affecting Tumor Growth and Metastasis in Preclinical In Vivo Models.Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2019 Nov-Dec;16(6):451-464. doi: 10.21873/cgp.20149. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2019. PMID: 31659100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The function of microRNA related to cancer-associated fibroblasts in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Biochem Pharmacol. 2025 Jun;236:116849. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2025.116849. Epub 2025 Mar 6. Biochem Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40056941 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs in Metastasis and the Tumour Microenvironment.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 4;22(9):4859. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094859. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34064331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immuno-Surgical Management of Pancreatic Cancer with Analysis of Cancer Exosomes.Cells. 2020 Jul 9;9(7):1645. doi: 10.3390/cells9071645. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32659892 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling the contribution of tumor-associated macrophages in driving epithelial-mesenchymal transition: a review of mechanisms and therapeutic Strategies.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 2;15:1404687. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1404687. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39286635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) and Pancreatic Cancer: From the Role of EVs to the Interference with EV-Mediated Reciprocal Communication.Biomedicines. 2020 Aug 3;8(8):267. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8080267. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 32756339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The miRNA-21-5p Payload in Exosomes from M2 Macrophages Drives Tumor Cell Aggression via PTEN/Akt Signaling in Renal Cell Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 10;23(6):3005. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063005. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35328425 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

