Synergistic killing effects of homoharringtonine and arsenic trioxide on acute myeloid leukemia stem cells and the underlying mechanisms
- PMID: 31307525
- PMCID: PMC6631946
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-019-1295-8
Synergistic killing effects of homoharringtonine and arsenic trioxide on acute myeloid leukemia stem cells and the underlying mechanisms
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Synergistic killing effects of homoharringtonine and arsenic trioxide on acute myeloid leukemia stem cells and the underlying mechanisms.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Sep 16;38(1):407. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1377-7. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31526386 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: At present, it is generally believed that leukemia stem cells are the source of AML, so the killing of leukemia stem cells has become important. Previous studies have suggested that HHT combined with ATO can synergistically kill U937 cells, and HHT has also demonstrated the ability to kill leukemia stem cells. We evaluated whether HHT combined with ATO can systematically kill leukemia stem cells (LSCs) and explored the synergistic effect and molecular mechanism.
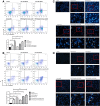
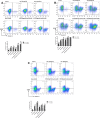
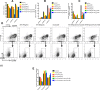
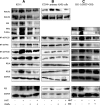
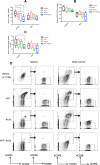
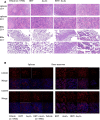
Methods: CCK-8 was used to detect cell viability. The changes of cell cycle (PI staining), apoptosis (Annexin V/PI) and surface markers (CD34, CD38, CD96, CD45) were detected by flow cytometry. The cells of CD34+ primary leukemia and CD38- KG-1, and TF-1 were separated by flow cytometry. High-throughput mRNA sequencing was used to analysis mRNA level changes after the application of the two drugs. Western blot was used to verify the changes of pathway protein expression. NRG mice were used as the receptor of xenograft model. Histological H&E staining assess the invaded ability of leukemia cells, and laser scanning confocal microscopy evaluated the molecule markers change.
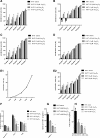
Results: HHT and ATO synergistically killed KG-1 (CD34+/CD96+/CD38+/-) and Kasumi-1 (CD34+/CD38-) cells. Their combination had a stronger effect of inducing apoptosis and blocking the cell cycle than HHT or ATO administrator alone, meanwhile significantly reducing the numbers of LSCs. Further, CD34+CD38- cells in KG-1, KG-1a, TF-1, and primary leukemia cells were more sensitive to HHT and ATO. High-throughput mRNA sequencing suggested that HHT alone could significantly upregulate molecules related to the Notch, P53, and NF-κB signaling pathways. When combined with ATO, HHT further upregulated P53, whereas HHT-induced NF-κB pathway activation was significantly suppressed. Western blot analysis verified the change of protein expression in the above pathways and further demonstrated that GSI, could eliminate these effects. In vivo, HHT combined with ATO significantly reduced the LSC burden, and weakened the expression of LSC markers.
Conclusions: This is the first evidence that HHT combined with arsenic can synergistically kill LSCs in vitro and in vivo, along with identification of the underlying mechanism, highlighting a potentially effective treatment strategy.
Keywords: Arsenic trioxide; Homoharringtonine; LSC; Notch; Xenograft leukemia model.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

