Identification of a potent small-molecule inhibitor of bacterial DNA repair that potentiates quinolone antibiotic activity in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 31307763
- PMCID: PMC6892255
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmc.2019.06.025
Identification of a potent small-molecule inhibitor of bacterial DNA repair that potentiates quinolone antibiotic activity in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
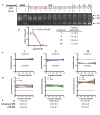
The global emergence of antibiotic resistance is one of the most serious challenges facing modern medicine. There is an urgent need for validation of new drug targets and the development of small molecules with novel mechanisms of action. We therefore sought to inhibit bacterial DNA repair mediated by the AddAB/RecBCD protein complexes as a means to sensitize bacteria to DNA damage caused by the host immune system or quinolone antibiotics. A rational, hypothesis-driven compound optimization identified IMP-1700 as a cell-active, nanomolar potency compound. IMP-1700 sensitized multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus to the fluoroquinolone antibiotic ciprofloxacin, where resistance results from a point mutation in the fluoroquinolone target, DNA gyrase. Cellular reporter assays indicated IMP-1700 inhibited the bacterial SOS-response to DNA damage, and compound-functionalized Sepharose successfully pulled-down the AddAB repair complex. This work provides validation of bacterial DNA repair as a novel therapeutic target and delivers IMP-1700 as a tool molecule and starting point for therapeutic development to address the pressing challenge of antibiotic resistance.
Keywords: Antibiotic resistance; DNA repair; Drug synergy; IMP-1700; Target validation.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information
Medical

