Interference with Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum Sensing and Virulence by the Mycobacterial Pseudomonas Quinolone Signal Dioxygenase AqdC in Combination with the N-Acylhomoserine Lactone Lactonase QsdA
- PMID: 31308081
- PMCID: PMC6759295
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00278-19
Interference with Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum Sensing and Virulence by the Mycobacterial Pseudomonas Quinolone Signal Dioxygenase AqdC in Combination with the N-Acylhomoserine Lactone Lactonase QsdA
Abstract
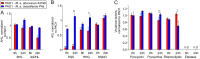
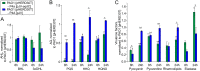
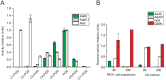
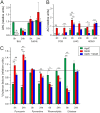
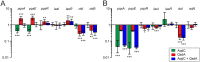
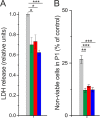
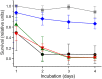
The nosocomial pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa regulates its virulence via a complex quorum sensing network, which, besides N-acylhomoserine lactones, includes the alkylquinolone signal molecules 2-heptyl-3-hydroxy-4(1H)-quinolone (Pseudomonas quinolone signal [PQS]) and 2-heptyl-4(1H)-quinolone (HHQ). Mycobacteroides abscessus subsp. abscessus, an emerging pathogen, is capable of degrading the PQS and also HHQ. Here, we show that although M. abscessus subsp. abscessus reduced PQS levels in coculture with P. aeruginosa PAO1, this did not suffice for quenching the production of the virulence factors pyocyanin, pyoverdine, and rhamnolipids. However, the levels of these virulence factors were reduced in cocultures of P. aeruginosa PAO1 with recombinant M. abscessus subsp. massiliense overexpressing the PQS dioxygenase gene aqdC of M. abscessus subsp. abscessus, corroborating the potential of AqdC as a quorum quenching enzyme. When added extracellularly to P. aeruginosa cultures, AqdC quenched alkylquinolone and pyocyanin production but induced an increase in elastase levels. When supplementing P. aeruginosa cultures with QsdA, an enzyme from Rhodococcus erythropolis which inactivates N-acylhomoserine lactone signals, rhamnolipid and elastase levels were quenched, but HHQ and pyocyanin synthesis was promoted. Thus, single quorum quenching enzymes, targeting individual circuits within a complex quorum sensing network, may also elicit undesirable regulatory effects. Supernatants of P. aeruginosa cultures grown in the presence of AqdC, QsdA, or both enzymes were less cytotoxic to human epithelial lung cells than supernatants of untreated cultures. Furthermore, the combination of both aqdC and qsdA in P. aeruginosa resulted in a decline of Caenorhabditis elegans mortality under P. aeruginosa exposure.
Keywords: Mycobacteroides abscessus; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Pseudomonas quinolone signal; dioxygenase; lactonase; quorum quenching enzyme; quorum sensing.
Copyright © 2019 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rhodococcus erythropolis BG43 Genes Mediating Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quinolone Signal Degradation and Virulence Factor Attenuation.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015 Nov;81(22):7720-9. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02145-15. Epub 2015 Aug 28. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26319870 Free PMC article.
-
Mycobacterium abscessus subsp. abscessus Is Capable of Degrading Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quinolone Signals.Front Microbiol. 2017 Mar 2;8:339. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00339. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28303132 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for recognition and ring-cleavage of the Pseudomonas quinolone signal (PQS) by AqdC, a mycobacterial dioxygenase of the α/β-hydrolase fold family.J Struct Biol. 2019 Sep 1;207(3):287-294. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2019.06.006. Epub 2019 Jun 19. J Struct Biol. 2019. PMID: 31228546
-
The third quorum-sensing system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Pseudomonas quinolone signal and the enigmatic PqsE protein.J Med Microbiol. 2020 Jan;69(1):25-34. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.001116. J Med Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31794380 Review.
-
Quorum sensing by 2-alkyl-4-quinolones in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other bacterial species.Mol Biosyst. 2008 Sep;4(9):882-8. doi: 10.1039/b803796p. Epub 2008 Jun 30. Mol Biosyst. 2008. PMID: 18704225 Review.
Cited by
-
Stabilizing AqdC, a Pseudomonas Quinolone Signal-Cleaving Dioxygenase from Mycobacteria, by FRESCO-Based Protein Engineering.Chembiochem. 2021 Feb 15;22(4):733-742. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202000641. Epub 2020 Nov 16. Chembiochem. 2021. PMID: 33058333 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial metabolism in the host and its association with virulence.Virulence. 2025 Dec;16(1):2459336. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2025.2459336. Epub 2025 Jan 31. Virulence. 2025. PMID: 39890585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural product-based inhibitors of quorum sensing: A novel approach to combat antibiotic resistance.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2025 Jun 24;43:102111. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2025.102111. eCollection 2025 Sep. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2025. PMID: 40641742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 17;21(22):8671. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228671. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33212950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights on the Pathogenesis of Mycobacterium abscessus Infection in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis.J Clin Med. 2025 May 16;14(10):3492. doi: 10.3390/jcm14103492. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40429486 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cystic Fibrosis Foundation. 2017. Annual data report 2016. Cystic fibrosis foundation patient registry. Cystic Fibrosis Foundation, Bethesda, MD.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

