RGS4 Maintains Chronic Pain Symptoms in Rodent Models
- PMID: 31308097
- PMCID: PMC6794935
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3154-18.2019
RGS4 Maintains Chronic Pain Symptoms in Rodent Models
Abstract
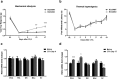
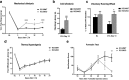
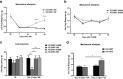
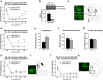
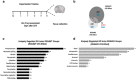
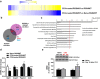
Regulator of G-protein signaling 4 (RGS4) is a potent modulator of G-protein-coupled receptor signal transduction that is expressed throughout the pain matrix. Here, we use genetic mouse models to demonstrate a role of RGS4 in the maintenance of chronic pain states in male and female mice. Using paradigms of peripheral inflammation and nerve injury, we show that the prevention of RGS4 action leads to recovery from mechanical and cold allodynia and increases the motivation for wheel running. Similarly, RGS4KO eliminates the duration of nocifensive behavior in the second phase of the formalin assay. Using the Complete Freud's Adjuvant (CFA) model of hindpaw inflammation we also demonstrate that downregulation of RGS4 in the adult ventral posterolateral thalamic nuclei promotes recovery from mechanical and cold allodynia. RNA sequencing analysis of thalamus (THL) from RGS4WT and RGS4KO mice points to many signal transduction modulators and transcription factors that are uniquely regulated in CFA-treated RGS4WT cohorts. Ingenuity pathway analysis suggests that several components of glutamatergic signaling are differentially affected by CFA treatment between RGS4WT and RGS4KO groups. Notably, Western blot analysis shows increased expression of metabotropic glutamate receptor 2 in THL synaptosomes of RGS4KO mice at time points at which they recover from mechanical allodynia. Overall, our study provides information on a novel intracellular pathway that contributes to the maintenance of chronic pain states and points to RGS4 as a potential therapeutic target.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT There is an imminent need for safe and efficient chronic pain medications. Regulator of G-protein signaling 4 (RGS4) is a multifunctional signal transduction protein, widely expressed in the pain matrix. Here, we demonstrate that RGS4 plays a prominent role in the maintenance of chronic pain symptoms in male and female mice. Using genetically modified mice, we show a dynamic role of RGS4 in recovery from symptoms of sensory hypersensitivity deriving from hindpaw inflammation or hindlimb nerve injury. We also demonstrate an important role of RGS4 actions in gene expression patterns induced by chronic pain states in the mouse thalamus. Our findings provide novel insight into mechanisms associated with the maintenance of chronic pain states and demonstrate that interventions in RGS4 activity promote recovery from sensory hypersensitivity symptoms.
Keywords: RGS; RNA sequencing; genetic mouse models; inflammatory pain; neuropathic pain; viral gene transfer.
Copyright © 2019 the authors.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
