A herpesvirus transactivator and cellular POU proteins extensively regulate DNA binding of the host Notch signaling protein RBP-Jκ to the virus genome
- PMID: 31308175
- PMCID: PMC6721950
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.007331
A herpesvirus transactivator and cellular POU proteins extensively regulate DNA binding of the host Notch signaling protein RBP-Jκ to the virus genome
Abstract
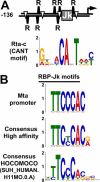
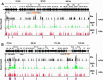
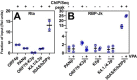
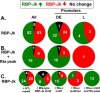
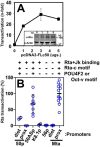
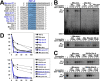
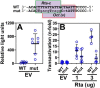
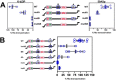
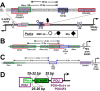
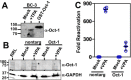
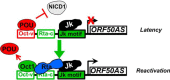
Reactivation of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) from latency requires the viral transactivator Rta to contact the host protein Jκ recombination signal-binding protein (RBP-Jκ or CSL). RBP-Jκ normally binds DNA sequence-specifically to determine the transcriptional targets of the Notch-signaling pathway, yet Notch alone cannot reactivate KSHV. We previously showed that Rta stimulates RBP-Jκ DNA binding to the viral genome. On a model viral promoter, this function requires Rta to bind to multiple copies of an Rta DNA motif (called "CANT" or Rta-c) proximal to an RBP-Jκ motif. Here, high-resolution ChIP/deep sequencing from infected primary effusion lymphoma cells revealed that RBP-Jκ binds nearly exclusively to different sets of viral genome sites during latency and reactivation. RBP-Jκ bound DNA frequently, but not exclusively, proximal to Rta bound to single, but not multiple, Rta-c motifs. To discover additional regulators of RBP-Jκ DNA binding, we used bioinformatics to identify cellular DNA-binding protein motifs adjacent to either latent or reactivation-specific RBP-Jκ-binding sites. Many of these cellular factors, including POU class homeobox (POU) proteins, have known Notch or herpesvirus phenotypes. Among a set of Rta- and RBP-Jκ-bound promoters, Rta transactivated only those that also contained POU motifs in conserved positions. On some promoters, POU factors appeared to inhibit RBP-Jκ DNA binding unless Rta bound to a proximal Rta-c motif. Moreover, POU2F1/Oct-1 expression was induced during KSHV reactivation, and POU2F1 knockdown diminished infectious virus production. Our results suggest that Rta and POU proteins broadly regulate DNA binding of RBP-Jκ during KSHV reactivation.
Keywords: DNA viruses; DNA-binding protein; KSHV; Notch pathway; Oct-1; POU2F1; Rta; chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChiP); herpesvirus; tumor virus; viral DNA.
© 2019 Gonzalez-Lopez et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures

Similar articles
-
The cellular Notch1 protein promotes KSHV reactivation in an Rta-dependent manner.J Virol. 2024 Aug 20;98(8):e0078824. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00788-24. Epub 2024 Jul 8. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38975769 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification of Direct RTA Targets Reveals Key Host Factors for Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Lytic Reactivation.J Virol. 2019 Feb 19;93(5):e01978-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01978-18. Print 2019 Mar 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30541837 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus reactivation is regulated by interaction of latency-associated nuclear antigen with recombination signal sequence-binding protein Jkappa, the major downstream effector of the Notch signaling pathway.J Virol. 2005 Mar;79(6):3468-78. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.6.3468-3478.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15731241 Free PMC article.
-
KSHV and the Role of Notch Receptor Dysregulation in Disease Progression.Pathogens. 2017 Aug 4;6(3):34. doi: 10.3390/pathogens6030034. Pathogens. 2017. PMID: 28777778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KSHV reactivation and novel implications of protein isomerization on lytic switch control.Viruses. 2015 Jan 12;7(1):72-109. doi: 10.3390/v7010072. Viruses. 2015. PMID: 25588053 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A SWI/SNF-dependent transcriptional regulation mediated by POU2AF2/C11orf53 at enhancer.Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 7;15(1):2067. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46492-5. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38453939 Free PMC article.
-
The cellular Notch1 protein promotes KSHV reactivation in an Rta-dependent manner.J Virol. 2024 Aug 20;98(8):e0078824. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00788-24. Epub 2024 Jul 8. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38975769 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Manifestations and Epigenetic Regulation of Oral Herpesvirus Infections.Viruses. 2021 Apr 15;13(4):681. doi: 10.3390/v13040681. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33920978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein Degradation by Gammaherpesvirus RTAs: More Than Just Viral Transactivators.Viruses. 2023 Mar 11;15(3):730. doi: 10.3390/v15030730. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36992439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KSHV RTA utilizes the host E3 ubiquitin ligase complex RNF20/40 to drive lytic reactivation.J Virol. 2023 Nov 30;97(11):e0138923. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01389-23. Epub 2023 Oct 27. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 37888983 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carbone A., Gaidano G., Gloghini A., Larocca L. M., Capello D., Canzonieri V., Antinori A., Tirelli U., Falini B., and Dalla-Favera R. (1998) Differential expression of BCL-6, CD138/syndecan-1, and Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein-1 identifies distinct histogenetic subsets of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-related non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. Blood 91, 747–755 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

