A newly developed anesthetic based on a unique chemical core
- PMID: 31308218
- PMCID: PMC6681746
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1822076116
A newly developed anesthetic based on a unique chemical core
Abstract
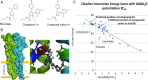
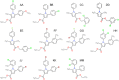
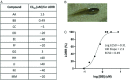
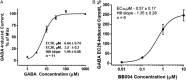
Intravenous anesthetic agents are associated with cardiovascular instability and poorly tolerated in patients with cardiovascular disease, trauma, or acute systemic illness. We hypothesized that a new class of intravenous (IV) anesthetic molecules that is highly selective for the slow type of γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor (GABAAR) could have potent anesthetic efficacy with limited cardiovascular effects. Through in silico screening using our GABAAR model, we identified a class of lead compounds that are N-arylpyrrole derivatives. Electrophysiological analyses using both an in vitro expression system and intact rodent hippocampal brain slice recordings demonstrate a GABAAR-mediated mechanism. In vivo experiments also demonstrate overt anesthetic activity in both tadpoles and rats with a potency slightly greater than that of propofol. Unlike the clinically approved GABAergic anesthetic etomidate, the chemical structure of our N-arylpyrrole derivative is devoid of the chemical moieties producing adrenal suppression. Our class of compounds also shows minimal to no suppression of blood pressure, in marked contrast to the hemodynamic effects of propofol. These compounds are derived from chemical structures not previously associated with anesthesia and demonstrate that selective targeting of GABAAR-slow subtypes may eliminate the hemodynamic side effects associated with conventional IV anesthetics.
Keywords: anesthesia; drug discovery; gamma amino butyric acid receptor; mechanism.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: E.J.B. and M.F.D. are coinventors on the patent WO 2016/061538 A1 “Novel Methods, Compounds, and Compositions for Anesthesia” and they, their department, and their institution could receive royalties related to the development of these new anesthetic agents.
Figures



Comment in
-
Computational Approaches to Anesthetic Drug Discovery.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Nov;40(11):809-811. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2019.09.001. Epub 2019 Oct 14. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31623940
Similar articles
-
In vivo and in vitro pharmacological studies of methoxycarbonyl-carboetomidate.Anesth Analg. 2012 Aug;115(2):297-304. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3182320559. Epub 2011 Sep 29. Anesth Analg. 2012. PMID: 21965364 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of GABA Receptors in Anesthesia and Sedation: An Updated Review.CNS Drugs. 2025 Jan;39(1):39-54. doi: 10.1007/s40263-024-01128-6. Epub 2024 Oct 27. CNS Drugs. 2025. PMID: 39465449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The anesthetic-like effects of diverse compounds on wild-type and mutant gamma-aminobutyric acid type A and glycine receptors.Anesth Analg. 2008 Mar;106(3):838-45, table of contents. doi: 10.1213/ane.0b013e31816095bd. Anesth Analg. 2008. PMID: 18292428
-
Mutations at beta N265 in γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptors alter both binding affinity and efficacy of potent anesthetics.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 27;9(10):e111470. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111470. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25347186 Free PMC article.
-
GABAA receptor: Positive and negative allosteric modulators.Neuropharmacology. 2018 Jul 1;136(Pt A):10-22. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.01.036. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Neuropharmacology. 2018. PMID: 29407219 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Dihydromyricetin and Metabolites in Serum and Brain Associated with Acute Anti-Ethanol Intoxicating Effects in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 12;22(14):7460. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147460. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34299083 Free PMC article.
-
Photopharmacology of Ion Channels through the Light of the Computational Microscope.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 8;22(21):12072. doi: 10.3390/ijms222112072. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery of the EL-0052 as a potential anesthetic drug.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021 Jan 8;19:710-718. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.01.002. eCollection 2021. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 33510871 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Electroencephalographic Profile of a New Anesthetic and Anticonvulsant That Is Selective for the GABA A R Slow Receptor Subtype.Anesth Analg. 2025 Aug 1;141(2):412-421. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000007178. Epub 2024 Oct 4. Anesth Analg. 2025. PMID: 39466672
-
Modulation of α1β3γ2 GABAA receptors expressed in X. laevis oocytes using a propofol photoswitch tethered to the transmembrane helix.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Feb 23;118(8):e2008178118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2008178118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33593898 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fahrenbach V. S., Bertaccini E. J., Insights into receptor-based anesthetic pharmacophores and anesthetic-protein interactions. Methods Enzymol. 602, 77–95 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Wagner R. L., White P. F., Kan P. B., Rosenthal M. H., Feldman D., Inhibition of adrenal steroidogenesis by the anesthetic etomidate. N. Engl. J. Med. 310, 1415–1421 (1984). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

