BK channel clustering is required for normal behavioral alcohol sensitivity in C. elegans
- PMID: 31308408
- PMCID: PMC6629859
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-46615-9
BK channel clustering is required for normal behavioral alcohol sensitivity in C. elegans
Abstract
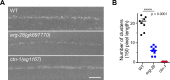
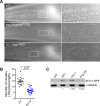
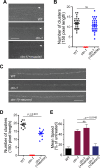
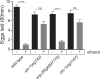
The large conductance, calcium- and voltage-activated potassium channel, known as the BK channel, is one of the central proteins that mediate alcohol intoxication and tolerance across species. Although ethanol targets BK channels through direct interaction, how ethanol-mediated BK channel activation causes behavioral intoxication is poorly understood. In. C. elegans, loss of function in SLO-1, the BK channel ortholog, confers profound ethanol resistance in movement and egg-laying behaviors. Here, we show that depletion of SLO-1 channels clustered at the active zones with no change in the overall channel expression level results in locomotory resistance to the intoxicating effect of ethanol, equivalent to that of slo-1 loss-of-function mutants. Likewise, depletion of clustered SLO-1 channels in the sarcolemma and neurons leads to ethanol-resistant egg-laying behavior. By contrast, reduction in the overall SLO-1 channel level by over 70% causes only moderate ethanol resistance in movement, and minimal, if any, resistance in egg laying. Our findings strongly suggest that behavioral ethanol sensitivity is conferred by local, but not global, depression of excitability via clustered BK channels. Given that clustered BK channels are functionally coupled to, and localize near, calcium channels, ethanol may mediate its behavioral effects by targeting BK channels and their coupled calcium channels.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Putative calcium-binding domains of the Caenorhabditis elegans BK channel are dispensable for intoxication and ethanol activation.Genes Brain Behav. 2015 Jul;14(6):454-65. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12229. Genes Brain Behav. 2015. PMID: 26113050 Free PMC article.
-
Conserved single residue in the BK potassium channel required for activation by alcohol and intoxication in C. elegans.J Neurosci. 2014 Jul 16;34(29):9562-73. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0838-14.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25031399 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral Deficits Following Withdrawal from Chronic Ethanol Are Influenced by SLO Channel Function in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2017 Jul;206(3):1445-1458. doi: 10.1534/genetics.116.193102. Epub 2017 May 25. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 28546434 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol interactions with calcium-dependent potassium channels.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2007 Oct;31(10):1625-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2007.00469.x. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2007. PMID: 17850640 Review.
-
Modulation of BK Channels by Ethanol.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2016;128:239-79. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2016.03.019. Epub 2016 May 12. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 27238266 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Alcohol induces mitochondrial fragmentation and stress responses to maintain normal muscle function in Caenorhabditis elegans.FASEB J. 2020 Jun;34(6):8204-8216. doi: 10.1096/fj.201903166R. Epub 2020 Apr 15. FASEB J. 2020. PMID: 32294300 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional analysis of the response of C. elegans to ethanol exposure.Sci Rep. 2021 May 26;11(1):10993. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-90282-8. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34040055 Free PMC article.
-
Large conductance voltage-and calcium-activated K+ (BK) channel in health and disease.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Mar 22;15:1373507. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1373507. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38584598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BK ZERO isoform HEK293 stably transfected cell lines differing 3'UTRs to assess miR-9 regulation.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 19;19(3):e0298966. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298966. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38502673 Free PMC article.
-
Hispidol Regulates Behavioral Responses to Ethanol through Modulation of BK Channels: A Novel Candidate for the Treatment of Alcohol Use Disorder.Molecules. 2024 Sep 24;29(19):4531. doi: 10.3390/molecules29194531. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39407462 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

