Oxidized carbon nanoparticles as an effective protein antigen delivery system targeting the cell-mediated immune response
- PMID: 31308663
- PMCID: PMC6618039
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S204134
Oxidized carbon nanoparticles as an effective protein antigen delivery system targeting the cell-mediated immune response
Abstract
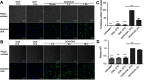
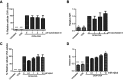
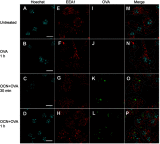
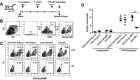
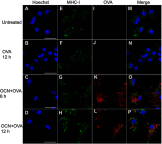
Background: The demand for an effective vaccine delivery system that drives a suitable immune response is increasing. The oxidized carbon nanosphere (OCN), a negatively charged carbon nanoparticle, has the potential to fulfill this requirement because it can efficiently deliver macromolecules into cells and allows endosomal leakage. However, fundamental insights into how OCNs are taken up by antigen-presenting cells, and the intracellular behavior of delivered molecules is lacking. Furthermore, how immune responses are stimulated by OCN-mediated delivery has not been investigated. Purpose: In this study, the model protein antigen ovalbumin (OVA) was used to investigate the uptake mechanism and intracellular fate of OCN-mediated delivery of protein in macrophages. Moreover, the immune response triggered by OVA delivered by OCNs was characterized. Methods: Bone-marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) from mice were used to study antigen uptake and intracellular trafficking. Mice were immunized using OCN-OVA combined with known adjuvants, and the specific immune response was measured. Results: OCNs showed no cytotoxicity against BMDMs. OCN-mediated delivery of OVA into BMDMs was partially temperature independent process. Using specific inhibitors, it was revealed that intracellular delivery of OCN-OVA does not rely on phagocytosis or the clathrin- and lipid raft/caveolae-mediated pathways. Delivered OVA was found to colocalize with compartments containing MHC class I, but not with early endosomes, lysosomes, and autophagosomes. Immunization of OVA using OCNs in combination with the known adjuvant monophosphoryl lipid A specifically enhanced interferon gamma (IFNγ)- and granzyme B-producing cytotoxic T cells (CTLs). Conclusion: OCNs effectively delivered protein antigens into macrophages that localized with compartments containing MHC class I partially by the temperature independent, but not clathrin- and lipid raft/caveolae-mediated pathways. Increased CD8+ T-cell activity was induced by OCN-delivered antigens, suggesting antigen processing toward antigen presentation for CTLs. Taken together, OCNs are a potential protein antigen delivery system that stimulates the cell-mediated immune response.
Keywords: adjuvant; cell-mediated immune response; macrophages; oxidized carbon nanosphere.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report that there are no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Oxidized Carbon Nanosphere-Based Subunit Vaccine Delivery System Elicited Robust Th1 and Cytotoxic T Cell Responses.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Mar 28;29(3):489-499. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1809.09049. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30691253
-
pH-Responsive Poly(D,L-lactic-co-glycolic acid) Nanoparticles with Rapid Antigen Release Behavior Promote Immune Response.ACS Nano. 2015 May 26;9(5):4925-38. doi: 10.1021/nn5066793. Epub 2015 Apr 24. ACS Nano. 2015. PMID: 25898266
-
Neutral polymer micelle carriers with pH-responsive, endosome-releasing activity modulate antigen trafficking to enhance CD8(+) T cell responses.J Control Release. 2014 Oct 10;191:24-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.03.041. Epub 2014 Mar 31. J Control Release. 2014. PMID: 24698946 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial antigen delivery systems: phagocytic processing of bacterial antigens for MHC-I and MHC-II presentation to T cells.Behring Inst Mitt. 1997 Feb;(98):197-211. Behring Inst Mitt. 1997. PMID: 9382741 Review.
-
Oligomannose-coated liposome as a novel adjuvant for the induction of cellular immune responses to control disease status.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:562924. doi: 10.1155/2013/562924. Epub 2013 Oct 10. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 24224170 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An Overview of Nanocarrier-Based Adjuvants for Vaccine Delivery.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Mar 27;13(4):455. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13040455. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 33801614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidized carbon black nanoparticles induce endothelial damage through C-X-C chemokine receptor 3-mediated pathway.Redox Biol. 2021 Nov;47:102161. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.102161. Epub 2021 Oct 4. Redox Biol. 2021. PMID: 34624601 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clark TG, Cassidy-Hanley D. Recombinant subunit vaccines: potentials and constraints. Dev Biol (Basel). 2005;121:153–163. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

