Rhein sensitizes human colorectal cancer cells to EGFR inhibitors by inhibiting STAT3 pathway
- PMID: 31308698
- PMCID: PMC6618855
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S206833
Rhein sensitizes human colorectal cancer cells to EGFR inhibitors by inhibiting STAT3 pathway
Abstract
Background: Activation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) has been reported in a variety of cancer types, including colorectal cancer (CRC), and represents a potential chemotherapeutic drug target. EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) have been increasingly applied in the clinical treatment of CRC, but development of drug resistance during the treatment has greatly limited their application. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and its mediated signal transduction pathway play an important role in the occurrence, development and metastasis of CRC, and are related to the development of EGFR-TKI resistance in CRC.
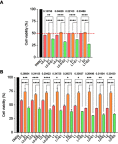
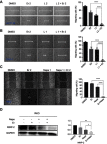
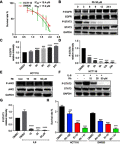
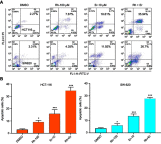
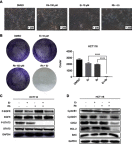
Methods: Cell viability, colony formation and cellular morphology were examined to evaluate the potent antiproliferative effect of the STAT3 inhibitor napabucasin, LY5 and rhein on the human CRC cell lines HCT116, SW620, RKO and DLD-1. Flow cytometry-based analysis was employed to determine whether rhein can affect the cell cycle and apoptosis. The expression level of phosphorylated STAT3 (P-STAT3), and cell cycle- and apoptosis-related proteins BCL2, CDC2 BAX, Cyclin D1 and Cyclin B1 were detected by Western blot analysis.
Results: This study revealed that rhein can significantly reduce cell viability and stimulate apoptosis in human CRC cells in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, rhein induced cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase in CRC cells and dose-dependently inhibited the expression of cell cycle-related proteins. Additionally, it was found that napabucasin, LY5 and rhein considerably sensitized cells to the EGFR-TKI erlotinib, thus suppressing CRC cell proliferation. Rhein also inhibited the phosphorylation of its downstream target STAT3. Inhibition of STAT3 and EGFR phosphorylation was also observed after treatment with a combination of rhein and EGFR inhibitors.
Conclusion: This study confirmed the synergistic effect of STAT3 inhibitor and EGFR inhibitor in CRC cell lines. Additionally, we found that rhein sensitizes human CRC cells to EGFR-TKIs by inhibiting STAT3 pathway. When combined with EGFR-TKIs, rhein may be a novel STAT3 inhibitor in CRC.
Keywords: EGFR; STAT3; colorectal cancer; rhein; tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rhein sensitizes human pancreatic cancer cells to EGFR inhibitors by inhibiting STAT3 pathway.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Jan 23;38(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-1015-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30674340 Free PMC article.
-
Rhein shows potent efficacy against non-small-cell lung cancer through inhibiting the STAT3 pathway.Cancer Manag Res. 2019 Feb 1;11:1167-1176. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S171517. eCollection 2019. Cancer Manag Res. 2019. PMID: 30774444 Free PMC article.
-
A novel STAT3 inhibitor W2014-S regresses human non-small cell lung cancer xenografts and sensitizes EGFR-TKI acquired resistance.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 1;11(2):824-840. doi: 10.7150/thno.49600. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33391507 Free PMC article.
-
STAT3 and the STAT3‑regulated inhibitor of apoptosis protein survivin as potential therapeutic targets in colorectal cancer (Review).Biomed Rep. 2024 Sep 24;21(6):175. doi: 10.3892/br.2024.1863. eCollection 2024 Dec. Biomed Rep. 2024. PMID: 39355529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plant-Derived Alkaloids as a Potential Source of Treatment for Colorectal Cancer over the Past Five Years: A Comprehensive Review.Plants (Basel). 2024 Sep 29;13(19):2723. doi: 10.3390/plants13192723. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39409593 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A biflavonoid-rich extract from Selaginella moellendorffii Hieron. induces apoptosis via STAT3 and Akt/NF-κB signalling pathways in laryngeal carcinoma.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Oct;24(20):11922-11935. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15812. Epub 2020 Sep 1. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32869923 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Traditional Chinese Medicine in combination with EGFR Inhibitors against Cancer.J Cancer. 2025 Jun 5;16(8):2595-2612. doi: 10.7150/jca.109420. eCollection 2025. J Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40535810 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination of UPLC-Q-TOF/MS and Network Pharmacology to Reveal the Mechanism of Qizhen Decoction in the Treatment of Colon Cancer.ACS Omega. 2021 May 26;6(22):14341-14360. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c01183. eCollection 2021 Jun 8. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 34124457 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Emergence of Rhein as a Potential Anticancer Drug: A Review of Its Molecular Targets and Anticancer Properties.Molecules. 2020 May 12;25(10):2278. doi: 10.3390/molecules25102278. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32408623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting STAT3 Signaling Pathway in Colorectal Cancer.Biomedicines. 2021 Aug 15;9(8):1016. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9081016. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34440220 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

