A comparative study of the quality of non-stimulated and stimulated tears in normal eye male subjects using the tear ferning test
- PMID: 31308779
- PMCID: PMC6613193
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTO.S214597
A comparative study of the quality of non-stimulated and stimulated tears in normal eye male subjects using the tear ferning test
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate and compare the tear ferning patterns of non-stimulated and stimulated tears in normal eye male subjects using the tear ferning test.
Methods: Thirty-five male subjects aged 20-38 years with normal eyes were enrolled in the study. Subjects with dry eye or with a risk factor for eye dryness (eg, recent ocular surgery, contact-lens wearers, smokers, anemic, diabetes, and thyroid gland problems) were excluded from the study. Dry eye subjects were excluded based on the ocular surface diseases index scores, non-invasive tear break-up time, and tear meniscus height measurements from the right and left eyes. A tear sample was collected from both eyes in each subject to perform the tear ferning test for non-stimulated tears. After 10 mins, the tears were stimulated using a Schirmer strip, a tear sample was collected from both eyes in each participant, the tear ferning test was performed, and the ferns were graded based on the five-point tear ferning grading scale.
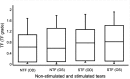
Results: The average tear ferning grade [median (interquartile range)] for non-stimulated tears from the right and left eyes was 0.60 (1.25) and 0.50 (1.31), respectively. For stimulated tears, the average tear ferning grade from the right and left eyes was 0.50 (1.05) and 0.75 (1.25), respectively. There was no significant difference in the tear ferning grades obtained from non-stimulated and stimulated tears (Wilcoxon test, P>0.05).
Conclusion: This study found no significant difference in the tear ferning patterns obtained from non-stimulated and stimulated tears, or between the tear ferning patterns in the tears collected from the right and left eyes before and after stimulating tears. It seems that there were no changes in the chemical composition of tears before and after stimulation, possibly due to the steady concentration of electrolytes and lipids within the tear film for both non-stimulated and stimulated tears.
Keywords: eye dryness; non-stimulated and stimulated tears; tear ferning patterns; tear film; tear quality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The use of tear ferning test in cats for evaluation of ocular surface.Acta Vet Scand. 2020 May 26;62(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s13028-020-00523-5. Acta Vet Scand. 2020. PMID: 32456655 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Refresh Plus® preservative-free lubricant eyedrops on tear ferning patterns in dry eye and normal eye subjects.Clin Ophthalmol. 2019 Jun 14;13:1011-1017. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S213365. eCollection 2019. Clin Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 31354235 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of the Addition of Electrolyte Solutions on the Ferning Patterns of Tears Collected from Normal Eye Subjects.Optom Vis Sci. 2022 May 1;99(5):463-469. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0000000000001897. Epub 2022 Mar 29. Optom Vis Sci. 2022. PMID: 35412507
-
Investigation of Ocular Tear Ferning in Controlled and Uncontrolled Diabetic Subjects.Eye Contact Lens. 2018 Nov;44 Suppl 2:S70-S75. doi: 10.1097/ICL.0000000000000419. Eye Contact Lens. 2018. PMID: 28945647
-
The tear ferning test: a simple clinical technique to evaluate the ocular tear film.Clin Exp Optom. 2014 Sep;97(5):399-406. doi: 10.1111/cxo.12160. Clin Exp Optom. 2014. PMID: 25138744 Review.
Cited by
-
The use of tear ferning test in cats for evaluation of ocular surface.Acta Vet Scand. 2020 May 26;62(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s13028-020-00523-5. Acta Vet Scand. 2020. PMID: 32456655 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Tear Ferning Patterns in Young Female Subjects with Refractive Errors.J Ophthalmol. 2021 Jan 23;2021:9524143. doi: 10.1155/2021/9524143. eCollection 2021. J Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 33552597 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Analysis of Tear Composition in Humans, Domestic Mammals, Reptiles, and Birds.Front Vet Sci. 2020 May 22;7:283. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00283. eCollection 2020. Front Vet Sci. 2020. PMID: 32528986 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement in Tear Ferning Patterns of Sheep Tears After Addition of Various Electrolyte Solutions.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Nov 19;8:721969. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.721969. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34869419 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in clinical examination of lacrimal gland.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Aug 31;10:1257209. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1257209. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37720501 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

