'If you can't see a dilemma in this situation you should probably regard it as a warning': a metasynthesis and theoretical modelling of general practitioners' opioid prescription experiences in primary care
- PMID: 31308941
- PMCID: PMC6613071
- DOI: 10.1177/2049463718804572
'If you can't see a dilemma in this situation you should probably regard it as a warning': a metasynthesis and theoretical modelling of general practitioners' opioid prescription experiences in primary care
Abstract
Introduction: The prescribing of opioids has increased internationally in developed countries in recent decades within primary and secondary care. The majority of patients with chronic non-malignant pain (CNMP) are managed by their general practitioner (GP). Recent qualitative studies have examined the issue of opioid prescribing for CNMP from a GP viewpoint. The aim of this study is to identify and synthesise the qualitative literature describing the factors influencing the nature and extent of opioid prescribing by GPs for patients with CNMP in primary care.
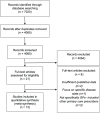
Methods: MEDLINE, Embase, PsycINFO, Cochrane Database, International Pharmaceutical Abstracts, Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects, CINAHL and Web of Science were systematically searched from January 1986 to February 2018. The full text of included articles was reviewed using the Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP) tool for qualitative research. The papers were coded by two researchers and themes organised using Thematic Network Analysis. Themes were constructed in a hierarchical manner, basic themes informed organising themes which informed global themes. A theoretical model was derived using global themes to explain the interplay between factors influencing opioid prescribing decisions.
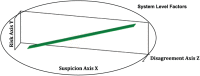
Results: From 7020 records, 21 full text papers were assessed, and 13 studies included in the synthesis; 9 were from the United States, 3 from the United Kingdom and 1 from Canada. Four global themes emerged: suspicion, risk, agreement and encompassing systems level factors. These global themes are inter-related and capture the complex decision-making processes underlying opioid prescribing whereby the physician both consciously and unconsciously quantifies the risk-benefit relationship associated with initiating or continuing an opioid prescription.
Conclusion: Recognising the inherent complexity of opioid prescribing and the limitations of healthcare systems is crucial to developing opioid stewardship strategies to combat the rise in opioid prescription morbidity and mortality.
Keywords: Chronic pain; family medicine; general practitioner; opioid; prescribing metasynthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
General practitioners' attitudes towards opioids for non-cancer pain: a qualitative systematic review.BMJ Open. 2022 Feb 1;12(2):e054945. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-054945. BMJ Open. 2022. PMID: 35105588 Free PMC article.
-
Qualitative insights into the opioid prescribing practices of Australian GP.Fam Pract. 2020 Jul 23;37(3):412-417. doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmz083. Fam Pract. 2020. PMID: 31768532
-
Healthcare stakeholders' perceptions and experiences of factors affecting the implementation of critical care telemedicine (CCT): qualitative evidence synthesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Feb 18;2(2):CD012876. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012876.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33599282 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review of Interventions and Programs Targeting Appropriate Prescribing of Opioids.Pain Physician. 2019 May;22(3):229-240. Pain Physician. 2019. PMID: 31151331
Cited by
-
A qualitative interview study exploring the experiences of pain specialists on prescribing opioids for chronic non-cancer pain.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 13;15(1):29672. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-15113-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40804328 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosing and managing prescription opioid use disorder in patients prescribed opioids for chronic pain in Australian general practice settings: a qualitative study using the theory of Planned Behaviour.BMC Prim Care. 2024 Jul 3;25(1):236. doi: 10.1186/s12875-024-02474-6. BMC Prim Care. 2024. PMID: 38961328 Free PMC article.
-
A pharmacist-led intervention to improve the management of opioids in a general practice: a qualitative evaluation of participant interviews.Int J Clin Pharm. 2022 Feb;44(1):235-246. doi: 10.1007/s11096-021-01340-0. Epub 2021 Nov 9. Int J Clin Pharm. 2022. PMID: 34751891
-
Changing or validating physician opioid prescribing behaviors through audit and feedback and academic detailing interventions in primary care.Implement Res Pract. 2025 Jan 7;6:26334895241307638. doi: 10.1177/26334895241307638. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. Implement Res Pract. 2025. PMID: 39780854 Free PMC article.
-
Opioid Treatment in Primary Care: Knowledge and Practical Use of Opioid Therapy.Healthcare (Basel). 2024 Jan 16;12(2):217. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12020217. Healthcare (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38255104 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De Conno F, Ripamonti C, Brunelli C. Opioid purchases and expenditure in nine western European countries: ‘are we killing off morphine? Palliative Med 2005; 19: 179–184. - PubMed
-
- Parsells Kelly J, Cook SF, Kaufman DW, et al. Prevalence and characteristics of opioid use in the US adult population. Pain 2008; 138: 507–513. - PubMed
-
- Ruscitto A, Smith BH, Guthrie B. Changes in opioid and other analgesic use 1995–2010: repeated cross-sectional analysis of dispensed prescribing for a large geographical population in Scotland. Eur J Pain 2015; 19: 59–66. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources