Dryopteris filix-mas (L.) Schott ethanolic leaf extract and fractions exhibited profound anti-inflammatory activity
- PMID: 31309077
- PMCID: PMC6612247
Dryopteris filix-mas (L.) Schott ethanolic leaf extract and fractions exhibited profound anti-inflammatory activity
Abstract
Objective: Dryopteris filix-mas (D. filix-mas) (L.) Schott, (Dryopteridaceae) is used in traditional medicine, particularly in the Southern parts of Nigeria for the treatment of inflammation, rheumatoid arthritis, wounds and ulcers. In this study, we evaluated the anti-inflammatory activity of its ethanolic leaf extract and fractions.
Materials and methods: The ethanolic leaf extract and fractions were screened for anti-inflammatory properties using egg-albumin-induced paw edema, xylene-induced topical ear edema, formaldehyde-induced arthritis and ulcerogenic models. The ethyl acetate most promising vacuum liquid chromatography fraction (VLC-E7) was purified using size exclusion chromatography technique (Sephadex LH-20) and its structure was elucidated using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and mass spectrometry. Total phenolic and flavonoid contents were also determined.
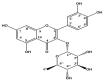
Results: From the study, ethyl acetate and butanol fractions elicited better anti-inflammatory activities in egg-albumin-induced paw edema, formaldehyde-induced arthritis and xylene-induced topical ear edema. The ethanol extract, ethyl acetate and butanol fractions were non-ulcerogenic at 200 and 400 mg/kg. The compound isolated from Sephadex fraction (SPH-E6) was quercetin-3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside.
Conclusion: Results of this study justify the ethnomedicinal use of D. filix-mas leaf for treatment of inflammation and rheumatoid arthritis. We suggest that D. filix-mas could be a prospective anti-inflammatory agent with no gastric irritation side effect, due to its bioactive component, quercetin-3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside.
Keywords: Anti-inflammatory; Dryopteris filix-mas; Non-ulcerogenic; Quercetin 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside; Rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Ajaghaku DL, Ilodigwe EE, Okonta MJ, Ogue CO, Okafor MA, Igboeme SO. Mechanism of anti-inflammatory activity of the leaf extract and fractions of Millettia aboensis. IRJP. 2013;4:54–59.
-
- Azubike NC, Okwuosa CN, Achukwu PU, Maduka TC, Chike O. Acute toxicity and histopathological effects of crude aqueous extract of Jatropha curcas leaves in mice. Res J Med Plant. 2015;9:340–346.
-
- Bafor EE, Omokaro WO, Uwumarongie OH, Elvis-Offiah UB, Omoruyi O, Viegelmann CV, Edrada-Ebel R. Dryopteris filix-mas (Dryopteridaceae) leaves inhibit mouse uterine activity. JOMPED. 2017;1:1–12.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
