First case report of latent tuberculosis reactivation complicating treatment with nilotinib in chronic myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 31309096
- PMCID: PMC6614099
- DOI: 10.5045/br.2019.54.2.151
First case report of latent tuberculosis reactivation complicating treatment with nilotinib in chronic myeloid leukemia
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' Disclosures of Potential Conflicts of Interest: No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
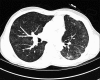
Figures

References
-
- Daniels JM, Vonk-Noordegraaf A, Janssen JJ, Postmus PE, van Altena R. Tuberculosis complicating imatinib treatment for chronic myeloid leukaemia. Eur Respir J. 2009;33:670–672. - PubMed
-
- Kang BW, Lee SJ, Moon JH, et al. Chronic myeloid leukemia patient manifesting fatal hepatitis B virus reactivation during treatment with imatinib rescued by liver transplantation: case report and literature review. Int J Hematol. 2009;90:383–387. - PubMed
-
- Mattiuzzi GN, Cortes JE, Talpaz M, et al. Development of Varicella-Zoster virus infection in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia treated with imatinib mesylate. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:976–980. - PubMed
-
- García-Muñoz R, Galar A, Moreno C, et al. Parvovirus B19 acute infection and a reactivation of cytomegalovirus and herpesvirus 6 in a chronic myeloid leukemia patient during treatment with dasatinib (BMS-354825) Leuk Lymphoma. 2007;48:2461–2464. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

