In Vitro Evaluation of the Biological Availability of Hyaluronic Acid Polyethylene Glycols-Cross-Linked Hydrogels to Bovine Testes Hyaluronidase
- PMID: 31309104
- PMCID: PMC6594335
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/3196723
In Vitro Evaluation of the Biological Availability of Hyaluronic Acid Polyethylene Glycols-Cross-Linked Hydrogels to Bovine Testes Hyaluronidase
Abstract
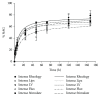
During last years, hyaluronic acid- (HA-) based dermal fillers have grown rapidly and continuously, as reported by the American Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery (ASAPS). In fact, HA fillers are considered the gold standard technique for soft tissue augmentation, deep skin hydration, and facial recontouring, playing a key role as an alternative to plastic surgery. HA fillers are less invasive, more biocompatible, and safer and with a more natural and immediate result if compared to plastic surgery. Hence, the safety of HA-based dermal fillers plays a crucial role, mostly in terms of biocompatibility and adjustability in case of unpleasant results and side effects such as, tyndall effect, edema, or granulomas. Hyaluronidase is a naturally occurring enzyme, present in the human body, and can degrade HA fillers avoiding more severe complications. In this article, we analyzed the bioavailability of hyaluronidase degradation of five fillers of Neauvia® hydrogels line (MatexLab SA, Lugano, CH), composed of pure hyaluronic acid and based on PEGDE cross-linking (polyethylene glycol) technology that guarantees a higher biocompatibility and an optimal biointegration and rheological characteristics. The performed in vitro testing is based on the colorimetric determination of the N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (NAG) present in solution after incubation with hyaluronidase, determined at different time points in order to assess the kinetic of each product degradation (1h, 3h, 6h, 24h, 48h, 72h, 120h, and 168h). The aim of this study was to assess, in vitro, how the difference in HA content and PEGDE concentration of the analyzed fillers can influence the product biocompatibility, intended as product enzymatic clearance and duration in time. The results demonstrated that the method was reproducible and easy to perform and that all the analyzed fillers are naturally immediately available for hyaluronidase-mediated degradation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
In Vitro Evaluation of the Sensitivity of a Hyaluronic Acid PEG Cross-Linked to Bovine Testes Hyaluronidase.Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2018 Jan 21;6(1):20-24. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2018.046. eCollection 2018 Jan 25. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 29483972 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative toxicity study of hyaluronic acid fillers crosslinked with 1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ether or poly (ethylene glycol) diglycidyl ether.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Mar;296:139620. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.139620. Epub 2025 Jan 7. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 39788250
-
Standardized in vitro analysis of the degradability of hyaluronic acid fillers by hyaluronidase.Eur J Med Res. 2018 Aug 20;23(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s40001-018-0334-9. Eur J Med Res. 2018. PMID: 30122153 Free PMC article.
-
Hyaluronidase: What is your fear?J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021 Oct;20(10):3169-3172. doi: 10.1111/jocd.14303. Epub 2021 Jul 19. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 34242464 Review.
-
The role of hyaluronidase in the treatment of complications from hyaluronic acid dermal fillers.Aesthet Surg J. 2013 Nov 1;33(8):1167-74. doi: 10.1177/1090820X13511970. Epub 2013 Nov 6. Aesthet Surg J. 2013. PMID: 24197934 Review.
Cited by
-
In Vitro Hair Growth Promoting Effect of a Noncrosslinked Hyaluronic Acid in Human Dermal Papilla Cells.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Oct 31;2021:5598110. doi: 10.1155/2021/5598110. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34754881 Free PMC article.
-
Model-Based Prediction to Evaluate Residence Time of Hyaluronic Acid Based Dermal Fillers.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jan 21;13(2):133. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13020133. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 33494145 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Evaluation of the Effect of a Not Cross-Linked Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel on Human Keratinocytes for Mesotherapy.Gels. 2021 Feb 4;7(1):15. doi: 10.3390/gels7010015. Gels. 2021. PMID: 33557183 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Pegylated Hyaluronic Acid Filler Enriched with Calcium Hydroxyapatite: A 24-Week Post-Market, Observational, Prospective, Open-Label, Single-Center Study.J Funct Biomater. 2023 Jun 29;14(7):345. doi: 10.3390/jfb14070345. J Funct Biomater. 2023. PMID: 37504840 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Neauvia Intense in Correcting Moderate-to-Severe Nasolabial Folds: A Post-Market, Prospective, Open-Label, Single-Centre Study.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2024 Jun 10;17:1351-1363. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S460973. eCollection 2024. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38881701 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

