Molecular basis of tRNA recognition by the Elongator complex
- PMID: 31309145
- PMCID: PMC6620098
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aaw2326
Molecular basis of tRNA recognition by the Elongator complex
Abstract
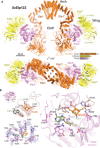
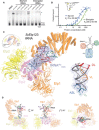
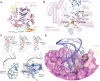
The highly conserved Elongator complex modifies transfer RNAs (tRNAs) in their wobble base position, thereby regulating protein synthesis and ensuring proteome stability. The precise mechanisms of tRNA recognition and its modification reaction remain elusive. Here, we show cryo-electron microscopy structures of the catalytic subcomplex of Elongator and its tRNA-bound state at resolutions of 3.3 and 4.4 Å. The structures resolve details of the catalytic site, including the substrate tRNA, the iron-sulfur cluster, and a SAM molecule, which are all validated by mutational analyses in vitro and in vivo. tRNA binding induces conformational rearrangements, which precisely position the targeted anticodon base in the active site. Our results provide the molecular basis for substrate recognition of Elongator, essential to understand its cellular function and role in neurodegenerative diseases and cancer.
Figures
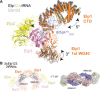

Similar articles
-
Structures and Activities of the Elongator Complex and Its Cofactors.Enzymes. 2017;41:117-149. doi: 10.1016/bs.enz.2017.03.001. Epub 2017 Apr 12. Enzymes. 2017. PMID: 28601220 Review.
-
Cryo-EM structure of the fully assembled Elongator complex.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Mar 21;51(5):2011-2032. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1232. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36617428 Free PMC article.
-
A conserved and essential basic region mediates tRNA binding to the Elp1 subunit of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Elongator complex.Mol Microbiol. 2014 Jun;92(6):1227-42. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12624. Epub 2014 May 19. Mol Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24750273 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of Elp1 by Hrr25 is required for elongator-dependent tRNA modification in yeast.PLoS Genet. 2015 Jan 8;11(1):e1004931. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004931. eCollection 2015 Jan. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 25569479 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into Elongator function.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2013 Apr;23(2):235-42. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2013.02.009. Epub 2013 Mar 16. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2013. PMID: 23510783 Review.
Cited by
-
Anticodon Wobble Uridine Modification by Elongator at the Crossroad of Cell Signaling, Differentiation, and Diseases.Epigenomes. 2020 May 12;4(2):7. doi: 10.3390/epigenomes4020007. Epigenomes. 2020. PMID: 34968241 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Links between TORC1 and Traditional Non-Coding RNA, tRNA.Genes (Basel). 2020 Aug 19;11(9):956. doi: 10.3390/genes11090956. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32825021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mössbauer-based molecular-level decomposition of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae ironome, and preliminary characterization of isolated nuclei.Metallomics. 2022 Nov 1;14(11):mfac080. doi: 10.1093/mtomcs/mfac080. Metallomics. 2022. PMID: 36214417 Free PMC article.
-
Elongator Subunit 3 (Elp3) Is Required for Zebrafish Trunk Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 31;21(3):925. doi: 10.3390/ijms21030925. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32023806 Free PMC article.
-
Sod1-deficient cells are impaired in formation of the modified nucleosides mcm5s2U and yW in tRNA.RNA. 2024 Nov 18;30(12):1586-1595. doi: 10.1261/rna.080181.124. RNA. 2024. PMID: 39322276 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tumaitis T. D., Lane B. G., Differential labelling of the carboxymethyl and methyl substituents of 5-carboxymethyluridine methyl ester, a trace nucleoside constituent of yeast transfer RNA. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 224, 391–403 (1970). - PubMed
-
- Paraskevopoulou C., Fairhurst S. A., Lowe D. J., Brick P., Onesti S., The elongator subunit Elp3 contains a Fe4S4 cluster and binds S-adenosylmethionine. Mol. Microbiol. 59, 795–806 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

