Dimerization of the Sodium/Iodide Symporter
- PMID: 31310151
- PMCID: PMC6797079
- DOI: 10.1089/thy.2019.0034
Dimerization of the Sodium/Iodide Symporter
Abstract
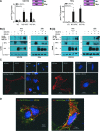
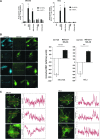
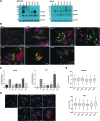
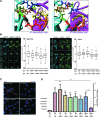
Background: The ability of thyroid follicular epithelial cells to accumulate iodide via the sodium/iodide symporter (NIS) is exploited to successfully treat most thyroid cancers, although a subset of patients lose functional NIS activity and become unresponsive to radioiodide therapy, with poor clinical outcome. Our knowledge of NIS regulation remains limited, however. While numerous membrane proteins are functionally regulated via dimerization, there is little definitive evidence of NIS dimerization, and whether this might impact upon radioiodide uptake and treatment success is entirely unknown. We hypothesized that NIS dimerizes and that dimerization is a prerequisite for iodide uptake. Methods: Coimmunoprecipitation, proximity ligation, and Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) assays were used to assess NIS:NIS interaction. To identify residues involved in dimerization, a homology model of NIS structure was built based on the crystal structure of the dimeric bacterial protein vSGLT. Results: Abundant cellular NIS dimerization was confirmed in vitro via three discrete methodologies. FRET and proximity ligation assays demonstrated that while NIS can exist as a dimer at the plasma membrane (PM), it is also apparent in other cellular compartments. Homology modeling revealed one key potential site of dimeric interaction, with six residues <3Å apart. In particular, NIS residues Y242, T243, and Q471 were identified as critical to dimerization. Individual mutation of residues Y242 and T243 rendered NIS nonfunctional, while abrogation of Q471 did not impact radioiodide uptake. FRET data show that the putative dimerization interface can tolerate the loss of one, but not two, of these three clustered residues. Conclusions: We show for the first time that NIS dimerizes in vitro, and we identify the key residues via which this happens. We hypothesize that dimerization of NIS is critical to its trafficking to the PM and may therefore represent a new mechanism that would need to be considered in overcoming therapeutic failure in patients with thyroid cancer.
Keywords: NIS; dimerization; radioiodide uptake; thyroid.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Schlumberger M, Brose M, Elisei R, Leboulleux S, Luster M, Pitoia F, Pacini F. 2014. Definition and management of radioactive iodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2:356–358 - PubMed
-
- Spitzweg C, Bible KC, Hofbauer LC, Morris JC. 2014. Advanced radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer: the sodium iodide symporter and other emerging therapeutic targets. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2:830–842 - PubMed
-
- American Thyroid Association Guidelines Taskforce on Thyroid Nodules, Differentiated Thyroid Cancer, Cooper DS, Doherty GM, Haugen BR, Kloos RT, Lee SL, Mandel SJ, Mazzaferri EL, McIver B, Pacini F, Schlumberger M, Sherman SI, Steward DL, Tuttle RM. 2009. Revised American Thyroid Association management guidelines for patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid 19:1167–1214 - PubMed
-
- La Vecchia C, Malvezzi M, Bosetti C, Garavello W, Bertuccio P, Levi F, Negri E. 2015. Thyroid cancer mortality and incidence: a global overview. Int J Cancer 136:2187–2195 - PubMed
-
- Ho AL, Grewal RK, Leboeuf R, Sherman EJ, Pfister DG, Deandreis D, Pentlow KS, Zanzonico PB, Haque S, Gavane S, Ghossein RA, Ricarte-Filho JC, Dominguez JM, Shen R, Tuttle RM, Larson SM, Fagin JA. 2013. Selumetinib-enhanced radioiodine uptake in advanced thyroid cancer. N Engl J Med 368:623–632 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
