Design optimization of high tibial osteotomy plates using finite element analysis for improved biomechanical effect
- PMID: 31311570
- PMCID: PMC6636153
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-019-1269-8
Design optimization of high tibial osteotomy plates using finite element analysis for improved biomechanical effect
Abstract
Background: High tibial osteotomy (HTO) is a common treatment for moderate osteoarthritis of the medial compartment in the knee joint by the translation of the force center toward the lateral compartment. However, the stability of a short plate such as Puddu used in this procedure was not as effective as other long plates such as Tomofix. No previous studies have used a rigorous and systematic design optimization method to determine the optimal shape of short HTO plate. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to evaluate the improved biomechanical stability of a short HTO plate by using design optimization and finite element (FE) analysis.
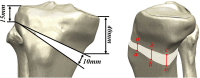
Methods: A FE model of HTO was subjected to physiological and surgical loads in the tibia. Taguchi-style L27 orthogonal arrays were used to identify the most significant factors for optimizing the design parameters. The optimal design variables were calculated using the nondominated sorting genetic algorithm II. Plate and bone stresses and wedge micromotions in the initial and optimized designs were chosen as the comparison indices.
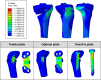
Results: Optimal designed HTO plate showed the decreased micromotions over the initial HTO plate with enhanced plate stability. In addition, increased bone stress and decreased plate stress supported the positive effect on stress shielding compared to initial HTO plate design. The results yielded a new short HTO design while demonstrating the feasibility of design optimization and potential improvements to biomechanical stability in HTO design. The newly developed short HTO plate throughout the optimization and computational simulation showed the improved biomechanical effect as good as the golden standard, TomoFix, does.
Conclusions: This study showed that plate design has a strong influence on the stability after HTO. This study demonstrated that the optimized short plates had low stress shielding effect and less micromotion because of its improvement in biomechanical performances. Our result showed that design optimization is an effective tool for HTO plate design. This information can aid future developments in HTO plate design and can be expanded to other implant designs.
Keywords: Design optimization; Finite element analysis; High tibial osteotomy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

