G-quadruplex ligand RHPS4 radiosensitizes glioblastoma xenograft in vivo through a differential targeting of bulky differentiated- and stem-cancer cells
- PMID: 31311580
- PMCID: PMC6636127
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-019-1293-x
G-quadruplex ligand RHPS4 radiosensitizes glioblastoma xenograft in vivo through a differential targeting of bulky differentiated- and stem-cancer cells
Abstract
Background: Glioblastoma is the most aggressive and most lethal primary brain tumor in the adulthood. Current standard therapies are not curative and novel therapeutic options are urgently required. Present knowledge suggests that the continued glioblastoma growth and recurrence is determined by glioblastoma stem-like cells (GSCs), which display self-renewal, tumorigenic potential, and increased radio- and chemo-resistance. The G-quadruplex ligand RHPS4 displays in vitro radiosensitizing effect in GBM radioresistant cells through the targeting and dysfunctionalization of telomeres but RHPS4 and Ionizing Radiation (IR) combined treatment efficacy in vivo has not been explored so far.
Methods: RHPS4 and IR combined effects were tested in vivo in a heterotopic mice xenograft model and in vitro in stem-like cells derived from U251MG and from four GBM patients. Cell growth assays, cytogenetic analysis, immunoblotting, gene expression and cytofluorimetric analysis were performed in order to characterize the response of differentiated and stem-like cells to RHPS4 and IR in single and combined treatments.
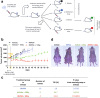
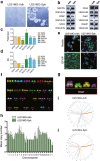
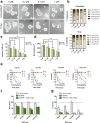
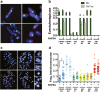
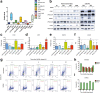
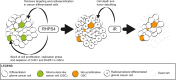
Results: RHPS4 administration and IR exposure is very effective in blocking tumor growth in vivo up to 65 days. The tumor volume reduction and the long-term tumor control suggested the targeting of the stem cell compartment. Interestingly, RHPS4 treatment was able to strongly reduce cell proliferation in GSCs but, unexpectedly, did not synergize with IR. Lack of radiosensitization was supported by the GSCs telomeric-resistance observed as the total absence of telomere-involving chromosomal aberrations. Remarkably, RHPS4 treatment determined a strong reduction of CHK1 and RAD51 proteins and transcript levels suggesting that the inhibition of GSCs growth is determined by the impairment of the replication stress (RS) response and DNA repair.
Conclusions: We propose that the potent antiproliferative effect of RHPS4 in GSCs is not determined by telomeric dysfunction but is achieved by the induction of RS and by the concomitant depletion of CHK1 and RAD51, leading to DNA damage and cell death. These data open to novel therapeutic options for the targeting of GSCs, indicating that the combined inhibition of cell-cycle checkpoints and DNA repair proteins provides the most effective means to overcome resistance of GSC to genotoxic insults.
Keywords: G4 ligands; Glioma stem-like cells; RHPS4; Radiosensitization; Telomeres.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

