Complete recovery of filler-induced visual loss following subcutaneous hyaluronidase injection
- PMID: 31312234
- PMCID: PMC6619934
- DOI: 10.1080/01658107.2018.1482358
Complete recovery of filler-induced visual loss following subcutaneous hyaluronidase injection
Abstract
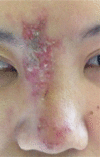
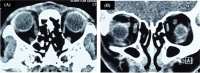
The rise in popularity of hyaluronic acid (HA) dermal filler injection has caused an exceptional increase in the number of cases of reported irreversible blindness. Here, we reported a case of ischemic optic neuropathy and ophthalmoplegia following subcutaneous HA filler injection with complete visual recovery. A 31-year-old Chinese woman presented with sudden onset of right monocular visual impairment associated with diplopia. Patient had received a hyaluronic acid-containing filler injection for nasal dorsum augmentation twelve hours prior to presentation. Visual acuity of the right eye was counting finger. A right relative afferent pupillary defect was demonstrated with ophthalmoplegia. Humphrey visual field test disclosed a right inferior altitudinal field defect with impairment of colour vision. Computed tomography of the orbit revealed mild enlargement of the right medial and inferior recti muscles. Our patient showed a tremendous improvement of vision after a subcutaneous hyaluronidase injection with complete visual recovery within 2 weeks.
Keywords: Hyaluronic acid injection; hyaluronidase; ischemic optic neuropathy; ophthalmoplegia.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
