Acute Myeloid Leukemia Acquiring Promyelocytic Leukemia-Retinoic Acid Receptor Alpha at Relapse
- PMID: 31312283
- PMCID: PMC6615911
- DOI: 10.14740/wjon1211
Acute Myeloid Leukemia Acquiring Promyelocytic Leukemia-Retinoic Acid Receptor Alpha at Relapse
Abstract
Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) is identified as the M3 subtype of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). APL is presently one of the most curable leukemias. We describe here a rare case of APL who presented as a relapsed disease after 1 year of chemotherapy for AML. The patient lacked t(15;17) at the initial presentation but was present later at the time of relapse. The patient attained a complete remission following treatment with all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) and arsenic trioxide-based therapy. We discuss the possible mechanism behind secondary acquisition of promyelocytic leukemia/retinoic acid receptor alpha (PML-RARA) at relapse of AML. We also briefly discuss the clinical features, diagnosis and treatment of APL.
Keywords: Acute myeloid leukemia; Acute promyelocytic leukemia; All-trans retinoic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
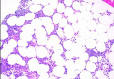

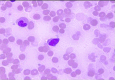
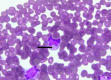
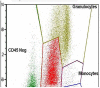
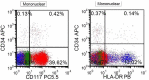
References
-
- Bernard J. History of promyelocytic leukaemia. Leukemia. 1994;8(Suppl 2):S1–5. - PubMed
-
- Shen ZX, Chen GQ, Ni JH, Li XS, Xiong SM, Qiu QY, Zhu J. et al. Use of arsenic trioxide (As2O3) in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL): II. Clinical efficacy and pharmacokinetics in relapsed patients. Blood. 1997;89(9):3354–3360. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
