HIV Testing and Treatment with the Use of a Community Health Approach in Rural Africa
- PMID: 31314966
- PMCID: PMC6748325
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1809866
HIV Testing and Treatment with the Use of a Community Health Approach in Rural Africa
Abstract
Background: Universal antiretroviral therapy (ART) with annual population testing and a multidisease, patient-centered strategy could reduce new human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infections and improve community health.
Methods: We randomly assigned 32 rural communities in Uganda and Kenya to baseline HIV and multidisease testing and national guideline-restricted ART (control group) or to baseline testing plus annual testing, eligibility for universal ART, and patient-centered care (intervention group). The primary end point was the cumulative incidence of HIV infection at 3 years. Secondary end points included viral suppression, death, tuberculosis, hypertension control, and the change in the annual incidence of HIV infection (which was evaluated in the intervention group only).
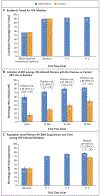
Results: A total of 150,395 persons were included in the analyses. Population-level viral suppression among 15,399 HIV-infected persons was 42% at baseline and was higher in the intervention group than in the control group at 3 years (79% vs. 68%; relative prevalence, 1.15; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.11 to 1.20). The annual incidence of HIV infection in the intervention group decreased by 32% over 3 years (from 0.43 to 0.31 cases per 100 person-years; relative rate, 0.68; 95% CI, 0.56 to 0.84). However, the 3-year cumulative incidence (704 incident HIV infections) did not differ significantly between the intervention group and the control group (0.77% and 0.81%, respectively; relative risk, 0.95; 95% CI, 0.77 to 1.17). Among HIV-infected persons, the risk of death by year 3 was 3% in the intervention group and 4% in the control group (0.99 vs. 1.29 deaths per 100 person-years; relative risk, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.64 to 0.93). The risk of HIV-associated tuberculosis or death by year 3 among HIV-infected persons was 4% in the intervention group and 5% in the control group (1.19 vs. 1.50 events per 100 person-years; relative risk, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.67 to 0.94). At 3 years, 47% of adults with hypertension in the intervention group and 37% in the control group had hypertension control (relative prevalence, 1.26; 95% CI, 1.15 to 1.39).
Conclusions: Universal HIV treatment did not result in a significantly lower incidence of HIV infection than standard care, probably owing to the availability of comprehensive baseline HIV testing and the rapid expansion of ART eligibility in the control group. (Funded by the National Institutes of Health and others; SEARCH ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT01864603.).
Copyright © 2019 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures

Comment in
-
HIV-1 Epidemic Control - Insights from Test-and-Treat Trials.N Engl J Med. 2019 Jul 18;381(3):286-288. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1907279. N Engl J Med. 2019. PMID: 31314975 No abstract available.
References
-
- The TEMPRANO ANRS 12136 Study Group. A trial of early antiretrovirals and isoniazid preventive therapy in Africa. N Engl J Med 2015;373:808–22. - PubMed
-
- Global AIDS update 2018: miles to go. Geneva: Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS), 2018.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- K23 MH114760/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH062246/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01AI099959/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases undefined/International
- UM1AI068636/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases undefined/International
- UM1 AI069496/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
