Glycosylation and its implications in breast cancer
- PMID: 31314995
- PMCID: PMC6702063
- DOI: 10.1080/14789450.2019.1645604
Glycosylation and its implications in breast cancer
Abstract
Introduction: For decades, the role of glycans and glycoproteins in the progression of breast cancer and other cancers have been evaluated. Through extensive studies focused on elucidating the biological functions of glycosylation, researchers have been able to implicate alterations in these functions to tumor formation and metastasis. Areas covered: In this review, we summarize how changes in glycosylation are associated with tumorigenesis, with emphasis on breast cancers. An overview of the changes in N-linked and O-linked glycans associated with breast cancer tumors and biofluids are described. Recent advances in glycomics are emphasized in the context of continuing to decipher the glycosylation changes associated with breast cancer progression. Expert opinion: While changes in glycosylation have been studied in breast cancer for many years, the clinical relevance of these studies has been limited. This reflects the inherent biological and clinical heterogeneity of breast cancers. Glycomics analysis lags behind the advances in genomics and proteomics, but new approaches are emerging. A summary of known glycosylation changes associated with breast cancer is necessary to implement new findings in the context of clinical outcomes and therapeutic strategies. A better understanding of the dynamics of tumor and immune glycosylation is critical to improving emerging immunotherapeutic treatments.
Keywords: Biomarkers; breast cancer; glycan; glycosylation; mass spectrometry.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interest
The authors have no relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. This includes employment, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, grants or patents received or pending, or royalties.
Figures


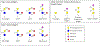

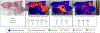
References
-
- Aub JC, Tieslau C, Lankester A. REACTIONS OF NORMAL AND TUMOR CELL SURFACES TO ENZYMES. I. WHEAT-GERM LIPASE AND ASSOCIATED MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDES. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1963. October;50:613–9. PubMed PMID: 14077487; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC221235. eng. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barton JG, Bois JP, Sarr MG, et al. Predictive and prognostic value of CA 19-9 in resected pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Journal of gastrointestinal surgery : official journal of the Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract. 2009. November;13(11):2050–8. doi: 10.1007/s11605-009-0849-z. PubMed PMID: 19756875; eng. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Drake RR. Glycosylation and Cancer: Moving Glycomics to the Forefront. Advances in cancer research. 2015;126:1–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
