Early Check: translational science at the intersection of public health and newborn screening
- PMID: 31315600
- PMCID: PMC6636013
- DOI: 10.1186/s12887-019-1606-4
Early Check: translational science at the intersection of public health and newborn screening
Abstract
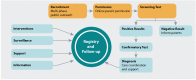
Background: Newborn screening (NBS) occupies a unique space at the intersection of translational science and public health. As the only truly population-based public health program in the United States, NBS offers the promise of making the successes of translational medicine available to every infant with a rare disorder that is difficult to diagnose clinically, but for which strong evidence indicates that presymptomatic treatment will substantially improve outcomes. Realistic NBS policy requires data, but rare disorders face a special challenge: Screening cannot be done without supportive data, but adequate data cannot be collected in the absence of large-scale screening. The magnitude and scale of research to provide this expanse of data require working with public health programs, but most do not have the resources or mandate to conduct research.
Methods: To address this gap, we have established Early Check, a research program in partnership with a state NBS program. Early Check provides the infrastructure needed to identify conditions for which there have been significant advances in treatment potential, but require a large-scale, population-based study to test benefits and risks, demonstrate feasibility, and inform NBS policy.
Discussion: Our goal is to prove the benefits of a program that can, when compared with current models, accelerate understanding of diseases and treatments, reduce the time needed to consider inclusion of appropriate conditions in the standard NBS panel, and accelerate future research on new NBS conditions, including clinical trials for investigational interventions.
Trial registration: Clinicaltrials.gov registration # NCT03655223 . Registered on August 31, 2018.
Keywords: Newborn screening; Rare disorders; Translational science.
Conflict of interest statement
The individual authors of this paper declare no competing interests. Early Check is supported in part by contributed reagents and equipment from Asuragen, but none of the authors has a personal or financial relationship with Asuragen.
References
-
- Kemper AR, Green NS, Calonge N, Lam WK, Comeau AM, Goldenberg AJ, et al. Decision-making process for conditions nominated to the recommended uniform screening panel: statement of the US Department of Health and Human Services Secretary’s advisory committee on heritable disorders in newborns and children. Genet Med. 2014;16(2):183–187. doi: 10.1038/gim.2013.98. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous