Oral levosimendan in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a phase II multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- PMID: 31315908
- PMCID: PMC6817985
- DOI: 10.1136/jnnp-2018-320288
Oral levosimendan in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a phase II multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of oral levosimendan in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). This phase II, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover, three-period study with 6 months open-label follow-up enrolled adults with ALS and sitting slow vital capacity (SVC) 60%-90 % of predicted from 11 sites in four countries.
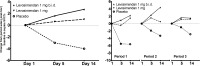
Methods: Patients received levosimendan 1 mg daily, 1 mg two times a day or placebo during three 14-day crossover periods and levosimendan 1-2 mg daily during open-label follow-up. Primary endpoint was sitting SVC; secondary endpoints included supine SVC, ALS Functional Rating Scale-Revised (ALSFRS-R), tolerability and safety.
Results: Of 66 patients randomised, 59 contributed to the double-blind results and 50 entered open-label follow-up. Sitting SVC was not significantly different between the treatments. In post hoc analysis using period-wise baselines, supine SVC favoured levosimendan over placebo, estimated mean differences from baseline being -3.62% on placebo, +0.77% on levosimendan 1 mg daily (p=0.018) and +2.38% on 1 mg two times a day (p=0.001). Headache occurred in 16.7% of patients during levosimendan 1 mg daily (p=0.030), 28.6% during 1 mg two times a day (p=0.002) and 3.3% during placebo. The respective frequencies for increased heart rate were 5.1% (p=0.337), 18.5% (p=0.018) and 1.7%. No significant differences between the treatments were seen for other adverse events.
Conclusions: Levosimendan did not achieve the primary endpoint of improving sitting SVC in ALS. Headache and increased heart rate were increased on levosimendan, although it was otherwise well tolerated. A phase III study to evaluate the longer term effects of oral levosimendan in ALS is ongoing.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02487407.
Keywords: SVC; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; levosimendan; respiratory function.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2019. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: VVA and TS are employees of Orion Corporation. Other authors have no conflicts to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Deschodt-Arsac V, Calmettes G, Raffard G, et al. Absence of mitochondrial activation during levosimendan inotropic action in perfused paced guinea pig hearts as demonstrated by modular control analysis. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2010;299:R786–R792. 10.1152/ajpregu.00184.2010 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
