Eukaryotic initiation factor 3, subunit C silencing inhibits cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis in human ovarian cancer cells
- PMID: 31316002
- PMCID: PMC6685053
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20191124
Eukaryotic initiation factor 3, subunit C silencing inhibits cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis in human ovarian cancer cells
Abstract
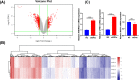
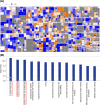
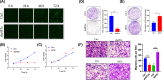
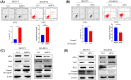
Ovarian cancer remains the leading cause of death among all gynaecological cancers, illustrating the urgent need to understand the molecular mechanisms involved in this disease. Eukaryotic initiation factor 3c (EIF3c) plays an important role in protein translation and cancer cell growth and proliferation, but its role in human ovarian cancer is unclear. Our results showed that EIF3c silencing significantly up-regulated 217 and down-regulated 340 genes. Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) indicated that the top differentially expressed genes are involved in 'Classical Pathways', 'Diseases and Functions' and 'Networks', especially those involved in signalling and cellular growth and proliferation. In addition, eIF3c silencing inhibited cellular proliferation, enhanced apoptosis and regulated the expression of apoptosis-associated proteins. In conclusion, these results indicate that by dysregulating translational initiation, eIF3c plays an important role in the proliferation and survival of human ovarian cancer cells. These results should provide experimental directions for further in-depth studies on important human ovarian cancer cell pathways.
Keywords: IPA; apoptosis; eIF3c; ovarian cancer cells,; proliferation.
© 2019 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

