RNA sequencing analysis revealed the induction of CCL3 expression in human intracranial aneurysms
- PMID: 31316152
- PMCID: PMC6637171
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-46886-2
RNA sequencing analysis revealed the induction of CCL3 expression in human intracranial aneurysms
Abstract
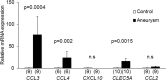
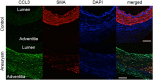
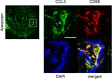
Intracranial aneurysm (IA) is a socially important disease as a major cause of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Recent experimental studies mainly using animal models have revealed a crucial role of macrophage-mediated chronic inflammatory responses in its pathogenesis. However, as findings from comprehensive analysis of unruptured human IAs are limited, factors regulating progression and rupture of IAs in humans remain unclear. Using surgically dissected human unruptured IA lesions and control arterial walls, gene expression profiles were obtained by RNA sequence analysis. RNA sequencing analysis was done with read count about 60~100 million which yielded 6~10 billion bases per sample. 79 over-expressed and 329 under-expressed genes in IA lesions were identified. Through Gene Ontology analysis, 'chemokine activity', 'defense response' and 'extracellular region' were picked up as over-represented terms which included CCL3 and CCL4 in common. Among these genes, quantitative RT-PCR analysis using another set of samples reproduced the above result. Finally, increase of CCL3 protein compared with that in control arterial walls was clarified in IA lesions. Findings of the present study again highlight importance of macrophage recruitment via CCL3 in the pathogenesis of IA progression.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was supported in part by Core Research for Evolutional Science and Technology Program (CREST) on ‘Mechanobiology’ from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED) (#JP18gm0810006, T.A.) and by the Coordination Fund from the Japanese Ministry for Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) and Astellas Pharma Inc. to Kyoto University (T.A. and S.N.). S.N. is supported by the Coordination Fund from MEXT and Astellas Pharma Inc. and T.A. was supported until 31th/March/2017. S.N. is a scientific advisor to Astellas Pharma. No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed by the other authors.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

