Pediatric elbow measurement parameters: Evaluation of the six angles in inter- and intra-observer reliability
- PMID: 31316257
- PMCID: PMC6612040
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcot.2018.07.019
Pediatric elbow measurement parameters: Evaluation of the six angles in inter- and intra-observer reliability
Abstract
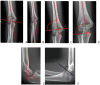
Background: Several radiographic measurements of the humerus can be used to evaluate the treatment outcome of supracondylar fractures in children. Because of the cartilaginous nature of the immature elbow, interpretation of radiographs around this area is sometimes challenging and can be unreliable. This study was conducted to determine the inter-observer and intra-observer reliability of the six commonly used radiographic measurements of the distal humerus.
Method: The Baumann angle, humero-ulna angle, metaphyseal-diaphyseal angle, radial epiphyseal angle, shaft-condylar angle and lateral capitellohumeral angle of the humerus were measured by two observers on the radiographs of uninjured elbows from 58 children. The values between each measurement were compared and correlated using a Pearson coefficient of correlation to determine the inter-observer and intra-observer reliability.
Results: All of the radiographic parameters showed excellent intra-observer reliability with the correlation coefficient values of the Baumann angle, humero-ulna angle, metaphyseal-diaphyseal angle, radial epiphyseal angle, shaft-condylar angle, lateral capitellohumeral angle as 0.945, 0.95, 0.909, 0.888, 0.961 and 0.975 (p < 0.001), respectively. The inter-observer reliability of the Baumann and humero-ulna angles were also found to be highly correlated at r = 0.843 (p < 0.001) and 0.878 (p < 0.001), respectively. The metaphyseal-diaphyseal angle had poor reliability with r = 0.136 (p = 0.291) while the radial epiphyseal angle, shaft-condylar angle, and lateral capitellohumeral angle demonstrated good reliability with r = 0.675 (p < 0.001), 0.747 (p < 0.001), and 0.686 (p < 0.001), respectively.
Conclusion: The Baumann angle and humero-ulna angle measurements of distal humerus showed excellent inter- and intra-observer reliability. Both parameters represent repeatable and reliable methods for determining the outcome of supracondylar humeral fractures in pediatric population.
Keywords: Baumann angle; Humero-ulna angle; Lateral capitellohumeral angle; Metaphyseal-diaphyseal angle; Radial-epiphyseal angle; Shaft-condylar angle.
Figures


References
-
- Williamson D.M., Coates C.J., Miller R.K., Cole W.G. Normal characteristics of the Baumann (humerocapitellar) angle: an aid in assessment of supracondylar fractures. J Pediatr Orthop. 1992 Sep-Oct;12(5):636–639. - PubMed
-
- Camp J., Ishizue K., Gomez M., Gelberman R., Akeson W. Alteration of Baumann's angle by humeral position: implications for treatment of supracondylar humerus fractures. J Pediatr Orthop. 1993 Jul-Aug;13(4):521–525. - PubMed
-
- Simanovsky N., Lamdan R., Hiller N., Simanovsky N. The measurement and standardization of humerocondylar angle in children. J Pediatr Orthop. 2008 Jun;28(4):463–465. - PubMed
-
- Beaty J.H., Kasser J.R. The elbow region: general concepts in the pediatric patient. In: Beaty J.H., Kasser J.R., editors. Rockwood and Wilkins Fractures in Children. seventh ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia, PA: 2010. pp. 563–576.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

