Body mass index and nipple preservation are major contributors to satisfaction and aesthetic outcome rates after implant-based immediate breast reconstruction
- PMID: 31316292
- PMCID: PMC6630387
- DOI: 10.5114/wo.2019.85881
Body mass index and nipple preservation are major contributors to satisfaction and aesthetic outcome rates after implant-based immediate breast reconstruction
Abstract
Introduction: Immediate breast reconstructions (IBR) have become an integral part of modern breast cancer management. However, in a small breast unit the spectrum of methods used for IBR could be limited, which could result in poorer results in some cases. The aim of the study is to evaluate the patient satisfaction and aesthetic outcome results in a breast unit where only implant-based IBR were performed.
Material and methods: During 2009-2016, 64 cases of implant-based IBR were performed in the university hospital. 55 patients completed the questionnaire and 38 underwent evaluation by a plastic surgeon. 33 skin-sparing and 22 nipple-sparing mastectomies were included. The study included 30 two-stage expander/implant and 25 direct-toimplant IBR cases.
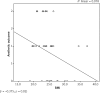
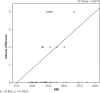
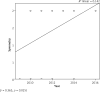
Results: Overall satisfaction was reported by 89% of respondents. 93% were satisfied with appearance in clothes and 82% with appearance in a bra. There was a significant difference with satisfaction in nude appearance between groups with a removed (3%) and a spared nipple (46%). The plastic surgeon evaluated overall outcome as satisfactory in 61% and poor in 39%. Spearman coefficient showed a moderate negative correlation between body mass index (BMI) and aesthetic outcome (p = 0.02), as well as BMI and volume differences between breasts (p = 0.03). Patients evaluated their breast symmetry as satisfactory in 55%, and the plastic surgeon concluded the same in 55% of 38 cases.
Conclusions: Most of the patients were satisfied with the aesthetic outcome of IBR. Nipple preservation considerably improved satisfaction rates. However, implant-based IBR revealed suboptimal cosmetic results in the subset of cases with increased BMI and other IBR methods should be considered in those cases.
Keywords: breast cancer; immediate breast reconstruction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Filiberti A, Rimoldi A, Callegari M, Nava M, Zanini V, Grisotti A. Immediate versus delayed breast reconstruction. A psychological answer. Eur J Plast Surg. 1990;13:55.
-
- Alderman AK, Kuhn LE, Lowery JC, Wilkins EG. Does patient satisfaction with breast reconstruction change over time? Two-year results of the Michigan Breast Reconstruction Outcomes Study. J Am Coll Surg. 2007;204:7–12. - PubMed
-
- Basta MN, Gerety PA, Serletti JM, Kovach SJ, Fischer JP. A Systematic Review and Head-to-Head Meta-Analysis of Outcomes following Direct-to-Implant versus Conventional Two-Stage Implant Reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015;136:1135–1144. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
