A Novel in vivo Anti-amnesic Agent, Specially Designed to Express Both Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) Inhibitory, Serotonergic Subtype 4 Receptor (5-HT4R) Agonist and Serotonergic Subtype 6 Receptor (5-HT6R) Inverse Agonist Activities, With a Potential Interest Against Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 31316368
- PMCID: PMC6611404
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2019.00148
A Novel in vivo Anti-amnesic Agent, Specially Designed to Express Both Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) Inhibitory, Serotonergic Subtype 4 Receptor (5-HT4R) Agonist and Serotonergic Subtype 6 Receptor (5-HT6R) Inverse Agonist Activities, With a Potential Interest Against Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
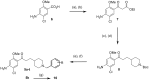
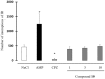
This work describes the conception, synthesis, in vitro and in vivo biological evaluation of novel Multi-Target Directed Ligands (MTDL) able to both activate 5-HT4 receptors, block 5-HT6 receptors and inhibit acetylcholinesterase activity (AChE), in order to exert a synergistic anti-amnesic effect, potentially useful in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Indeed, both activation of 5-HT4 and blockage of 5-HT6 receptors led to an enhanced acetylcholine release, suggesting it could lead to efficiently restoring the cholinergic neurotransmission deficit observed in AD. Furthermore, 5-HT4 receptor agonists are able to promote the non-amyloidogenic cleavage of the amyloid precursor protein (APP) and to favor the production of the neurotrophic protein sAPPα. Finally, we identified a pleiotropic compound, [1-(4-amino-5-chloro-2-methoxyphenyl)-3-(1-(3-methylbenzyl)piperidin-4-yl)propan-1-one fumaric acid salt (10)], which displayed in vivo an anti-amnesic effect in a model of scopolamine-induced deficit of working memory at a dose of 0.3 mg/kg.
Keywords: 5-HT4 receptors; 5-HT6 receptors; Alzheimer’s disease; MTDL; acetylcholinesterase.
Figures


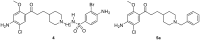



References
-
- Baranger K., Giannoni P., Girard S. D., Girot S., Gaven F., Stephan D., et al. . (2017). Chronic treatments with a 5-HT4 receptor agonist decrease amyloid pathology in the entorhinal cortex and learning and memory deficits in the 5xFAD mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropharmacology 126, 128–141. 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.08.031 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

