Markers of Coagulation and Fibrinolysis Predicting the Outcome of Acute Ischemic Stroke Thrombolysis Treatment: A Review of the Literature
- PMID: 31316444
- PMCID: PMC6611415
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00513
Markers of Coagulation and Fibrinolysis Predicting the Outcome of Acute Ischemic Stroke Thrombolysis Treatment: A Review of the Literature
Abstract
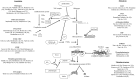
Intravenous administration of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rt-PA) has been proven to be safe and effective in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke. Little is known, however, why this treatment is less effective in some patients while in others life-threatening side-effects, e.g., symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage might occur. Clinical failure of thrombolysis related to absent or partial recanalization or reocclusion as well as hemorrhagic complications of thrombolysis are possibly related to hemostatic events. Data on markers of coagulation and/or fibrinolysis in acute stroke patients are numerous and may provide indications regarding therapy outcomes. Better understanding of the hemostatic and fibrinolytic system during rt-PA therapy might be clinically useful and ultimately might lead to an improvement in the efficacy or safety of this treatment. Studies on thrombus composition retrieved from cerebral arteries may also advance our knowledge and provide a key to improve acute stroke therapy. Here we provide a comprehensive review on a wide range of factors and markers of coagulation and fibrinolysis that have been studied in the context of thrombolysis outcome in ischemic stroke patients. Moreover, a brief summary is given on the most recent research on thrombus composition having a potential influence on outcomes.
Keywords: coagulation; fibrinolysis; outcome; stroke; thrombolysis.
Figures
References
-
- Ingall T. Stroke–incidence, mortality, morbidity and risk. J Insur Med. (2004) 36:143–52. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

