MicroRNA-191 targets CCAAT/enhanced binding protein β and functions as an oncogenic molecule in human non-small cell lung carcinoma cells
- PMID: 31316611
- PMCID: PMC6601399
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2019.7668
MicroRNA-191 targets CCAAT/enhanced binding protein β and functions as an oncogenic molecule in human non-small cell lung carcinoma cells
Abstract
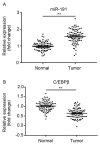
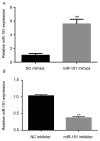
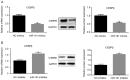
The aberrant expression of microRNAs (miRs) may be involved in tumor growth and progression in human non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). The present study aimed to investigate the potential roles of miR-191 in NSCLC. Western blotting and reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction were performed to assess protein and/or mRNA levels. Scratch wound healing and transwell assays were performed to determine the NSCLC cell migration and invasion. A luciferase demonstrated that CCAAT/enhanced binding protein β (C/EBPβ) was a target of miR-191. Previously, miR-191 has been reported to act as an oncogenic player in multiple human cancers. C/EBPβ has been identified as a target gene of miR-191; however, the roles and underlying mechanisms of miR-191 associated with the regulation of tumor invasion in NSCLC remain unknown. In the present study, it was demonstrated that miR-191 expression levels were higher in human NSCLC tumors compared with in normal adjacent tissue and elevated miR-191 expression levels were closely associated with tumor node metastasis stage in patients with NSCLC. Furthermore, transfection with miR-191 mimic inhibited C/EBPβ expression at the mRNA and protein levels and promoted A549 cell migration and invasion. C/EBPβ was reported to be the direct target gene of miR-191 using a dual luciferase reporter assay. Finally, C/EBPβ siRNA can mimic the effects of miR-191. These findings indicated that miR-191 may function as an oncogene in NSCLC, at least partially due to its negative regulatory on C/EBPβ.
Keywords: CCAAT/enhanced binding protein β; metastasis; microRNA-191; negative regulation; non-small cell lung carcinoma.
Figures



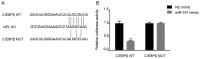
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
