β-catenin regulates effects of miR-24 on the viability and autophagy of glioma cells
- PMID: 31316620
- PMCID: PMC6601135
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2019.7680
β-catenin regulates effects of miR-24 on the viability and autophagy of glioma cells
Abstract
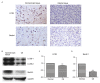
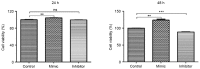
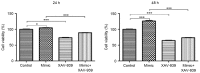
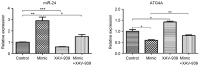
Mutations of the β-catenin gene are common in various cancer types. MicroRNA (miR)-24 suppresses gene expression during the cell cycle. However, the effects of miR-24 on the cell viability and autophagy of glioma cells, and how these biological processes are regulated by β-catenin are largely unclear. The current study aimed to investigate the role of β-catenin in regulating the effects of miR-24 on the cell viability and autophagy of glioma cells. The expression levels of microtubule-associated proteins 1A/1B light chain 3B (LC3B) and Beclin1 were detected by immunohistochemistry and western blotting. Glioma C6 cells were transfected with miR-24 mimics, miR-24 inhibitors and negative control miRNAs. C6 cells transfected with miR-24 mimics or negative control miRNAs were treated with the β-catenin inhibitor, XAV-939. An MTT assay was utilized to evaluate the viability of C6 cells. The expression of miR-24 and mRNA expression of autophagy related 4a cysteine peptidase (ATG4A) were detected by quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis. The protein expression of LC3B and Beclin1 decreased significantly in glioma tissue and glioma C6 cells compared with normal brain tissue. Compared with the negative control group, C6 cells transfected with miR-24 mimics exhibited significantly higher cell viability at 24 and 48 h, and those transfected with miR-24 inhibitors exhibited significantly lower cell viability at 48 h. XAV-939 decreased the stimulatory effects of miR-24 mimics on the viability of C6 cells. The expression of miR-24 significantly decreased and ATG4A mRNA significantly increased in C6 cells transfected with XAV-939 compared with those transfected with the negative control miRNA. XAV-939 attenuated the miR-24-induced decrease of the protein expression of LC3B and Beclin1, and decreased the stimulatory effects of miR-24 mimics on cell viability. In addition, XAV-939 attenuated the miR-24-induced decrease of autophagy marker expression by attenuating miR-24 expression and increasing ATG4A mRNA expression in glioma C6 cells. To the best of our knowledge, the present study is the first to demonstrate whether β-catenin regulates the intracellular effects of miR-24 on the viability and autophagy of glioma cells. The results also provide some mechanistic basis to the pharmaceutical targeting of WNT signaling in high grade glial tumors.
Keywords: autophagy; cell viability; glioma C6 cells; microRNA-24; β-catenin.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
