Spontaneous Otogenic Pneumocephalus: Case Series and Update on Management
- PMID: 31316888
- PMCID: PMC6635110
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0038-1676036
Spontaneous Otogenic Pneumocephalus: Case Series and Update on Management
Abstract
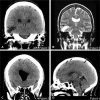
Objectives This study is aimed to report the largest independent case series of spontaneous otogenic pneumocephalus (SOP) and review its pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and treatment. Design Four patients underwent a middle cranial fossa approach for repair of the tegmen tympani and tegmen mastoideum. A comprehensive review of the literature regarding this disease entity was performed. Setting U.S. tertiary academic medical center. Participants: Patients presenting to the lead author's clinic or to the emergency department with radiographic evidence of SOP. Symptoms included headache, otalgia, and neurologic deficits. Main Outcome Measures Patients were assessed for length of stay, postoperative length of stay, and neurologic outcome. Three of four patients returned to their neurologic baseline following repair. Results Four patients were successfully managed via a middle cranial fossa approach to repairing the tegmen mastoideum. Conclusion The middle cranial fossa approach is an effective strategy to repair defects of the tegmen mastoideum. SOP remains a clinically rare disease, with little published information on its diagnosis and treatment.
Keywords: middle cranial fossa; otogenic; pneumocephalus; tegmen.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Stevens S M, Lambert P R, Rizk H, McIlwain W R, Nguyen S A, Meyer T A. Novel radiographic measurement algorithm demonstrating a link between obesity and lateral skull base attenuation. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015;152(01):172–179. - PubMed
-
- Goldmann R W. Pneumocephalus as a consequence of barotrauma. JAMA. 1986;255(22):3154–3156. - PubMed
-
- Markham J W. The clinical features of pneumocephalus based upon a survey of 284 cases with report of 11 additional cases. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1967;16(01):1–78. - PubMed
-
- Dandy W E. Pneumocephalus (intracranial pneumatocele or aerocele) Arch Surg. 1926;12:949–982.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

