Cognitive and functional progression of dementia in two longitudinal studies
- PMID: 31318090
- PMCID: PMC6803041
- DOI: 10.1002/gps.5175
Cognitive and functional progression of dementia in two longitudinal studies
Abstract
Objectives: Previous studies have identified several subgroups (ie, latent trajectories) with distinct disease progression among people with dementia. However, the methods and results were not always consistent. This study aims to perform a coordinated analysis of latent trajectories of cognitive and functional progression in dementia across two datasets.
Methods: Included and analyzed using the same statistical approach were 1628 participants with dementia from the US National Alzheimer's Coordinating Center (NACC) and 331 participants with dementia from the Dutch Clinical Course of Cognition and Comorbidity study (4C-Study). Trajectories of cognition and instrumental activities of daily living (IADL) were modeled jointly in a parallel-process growth mixture model.
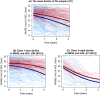
Results: Cognition and IADL tended to decline in unison across the two samples. Slow decline in both domains was observed in 26% of the US sample and 74% of the Dutch sample. Rapid decline in cognition and IADL was observed in 7% of the US sample and 26% of the Dutch sample. The majority (67%) of the US sample showed moderate cognitive decline and rapid IADL decline.
Conclusions: Trajectories of slow and rapid dementia progression were identified in both samples. Despite using the same statistical methods, the number of latent trajectories was not replicated and the relative class sizes differed considerably across datasets. These results call for careful consideration when comparing progression estimates in the literature. In addition, the observed discrepancy between cognitive and functional decline stresses the need to monitor dementia progression across multiple domains.
Keywords: cognition; coordinated analysis; daily functioning; dementia progression; growth mixture model; trajectory.
© 2019 The Authors. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Mayeux R, Stern Y, Spanton S. Heterogeneity in dementia of the Alzheimer type evidence of subgroups. Neurol. 1985;35(4):453. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt C, Wolff M, Weitz M, Bartlau T, Korth C, Zerr I. Rapidly progressive Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol. 2011;68(9):1124‐1130. - PubMed
-
- Cortes F, Nourhashémi F, Guérin O, et al. Prognosis of Alzheimer's disease today: a two‐year prospective study in 686 patients from the REAL‐FR Study. Alzheimers Dement. 2008;4(1):22‐29. - PubMed
-
- Behl P, Stefurak TL, Black SE. Progress in clinical neurosciences: cognitive markers of progression in Alzheimer's disease. Can J Neurol Sci Le journal canadien des sciences neurologiques. 2005;32(2):140‐151. - PubMed
-
- Cohen‐Mansfield J. Heterogeneity in dementia: challenges and opportunities. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2000;14(2):60‐63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P30 AG066507/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005142/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066515/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016573/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG047266/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG025688/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005138/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG047366/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG019610/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG033514/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013854/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG053760/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010124/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG023501/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005131/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005146/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG072122/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062421/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG035982/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG008702/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG016976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG008051/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013846/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG047270/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062429/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005136/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072973/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG049638/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG012300/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005134/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG008017/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062715/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010129/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066514/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG028383/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

